Job segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===== Date and country of first publication<ref>Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).</ref>===== | |||
1973<br> | |||
United States | |||
===== Definition ===== | |||
Job segregation refers to the practice of separating individuals into certain types of jobs based on their gender, race, age, or other protected characteristics. It is the result of discrimination and systemic biases in hiring practices and can contribute to unequal opportunities and treatment in the workplace. | Job segregation refers to the practice of separating individuals into certain types of jobs based on their gender, race, age, or other protected characteristics. It is the result of discrimination and systemic biases in hiring practices and can contribute to unequal opportunities and treatment in the workplace. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
Overall, job segregation is a detrimental practice that limits individual potential and hinders social progress. Creating inclusive workplaces where individuals of all backgrounds have equal opportunities for employment and advancement is crucial for creating a fair and equitable society. | Overall, job segregation is a detrimental practice that limits individual potential and hinders social progress. Creating inclusive workplaces where individuals of all backgrounds have equal opportunities for employment and advancement is crucial for creating a fair and equitable society. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
== | ==Related segregation forms== | ||
Job segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms: | |||
[[occupational segregation]], [[gender segregation]], [[sex segregation]], [[occupational gender segregation]], [[racial segregation]], [[social segregation]], [[black residential segregation]], [[black segregation]], [[residential segregation]], [[labor market segregation]], [[horizontal segregation]] | |||
[[File:job_segregation.png|780x780px]] | |||
This visualization is based on the study [[Segregation_Wiki:About| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | |||
==References== | |||
==Notes== | |||
<references /> | |||
{{NoteAI}} | |||
==Job segregation appears in the following literature== | |||
Marshall R. (1963). Some factors influencing the upgrading of negroes in the southern petroleu \1 refining industry. ''Social Forces'', ''42''(2), 186-195. https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/42.2.186 | |||
Stevenson M. (1973). Women's Wages and Job Segregation. ''Politics & Society'', ''4''(1), 83-96. https://doi.org/10.1177/003232927300400104 | |||
Wisniewski S.C. (1982). Achieving equal pay for comparable worth through arbitration.. ''Employee relations law journal'', ''8''(2), 236-255. https://doi.org/ | |||
Stahura J.M. (1983). Determinants of Change in the Distribution of Blacks across Suburbs. ''Sociological Quarterly'', ''24''(3), 421-433. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1533-8525.1983.tb00711.x | |||
Reskin B.F. (1988). Bringing the men back in: Sex Differentiation and the Devaluation of Women's Work. ''Gender & Society'', ''2''(1), 58-81. https://doi.org/10.1177/089124388002001005 | |||
Hensman R. (1988). The gender divisions of labour in manufacturing industry a case study in india. ''South Asia Research'', ''8''(2), 133-153. https://doi.org/10.1177/026272808800800203 | |||
Williams R.M., Smith P.R. (199). What else do unions do?: Race and gender in local 35. ''The Review of Black Political Economy'', ''18''(3), 59-74. Springer-Verlag.https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02717875 | |||
Hou J.W. (1991). Wage comparison by gender and the effect of job segregation: The case of Taiwan. ''China Economic Review'', ''2''(2), 195-214. https://doi.org/10.1016/1043-951X(91)90004-R | |||
Morgan G., Knights D. (1991). Gendering jobs: Corporate strategy, managerial control and the dynamics of job segregation. ''Work Employment & Society'', ''5''(2), 181-200. https://doi.org/10.1177/0950017091005002003 | |||
Grand C. (1991). Explaining the Male Female Wage Gap: Job Segregation and Solidarity Wage Bargaining in Sweden. ''Acta Sociologica'', ''34''(4), 261-277. https://doi.org/10.1177/000169939103400402 | |||
Hakim C. (1991). Grateful slaves and self made women: Fact and fantasy in women's work orientations. ''European Sociological Review'', ''7''(2), 101-121. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.esr.a036590 | |||
Devine F. (1993). Gender segregation and labour supply: On ‘choosing’ gender atypical jobs. ''British Journal of Education & Work'', ''6''(3), 61-74. https://doi.org/10.1080/0269000930060304 | |||
Tanski J.M. (1994). The impact of crisis, stabilization and structural adjustment on women in Lima, Peru. ''World Development'', ''22''(11), 1627-1642. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-750X(94)00073-5 | |||
Kenney S.J. (1994). Who Is Protected? What’s Wrong ith Exclusionary Policies. ''Women and Politics'', ''13''(3-4), 153-173. https://doi.org/10.1300/J014v13n03_10 | |||
Core F. (1994). Women and the restructuring of employment. ''OECD Observer'', ''186''(), 5-12. https://doi.org/ | |||
Hutton S. (1994). Men's and women's incomes: evidence from survey data. ''Journal of Social Policy'', ''23''(1), 21-40. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0047279400021309 | |||
Kulis S.S., Shaw H.E. (1996). Racial segregation among postsecondary workers. ''Social Forces'', ''75''(2), 575-591. University of North Carolina Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/75.2.575 | |||
Kulis S. (1997). Gender segregation among college and university employees. ''Sociology of Education'', ''70''(2), 151-173. American Sociological Association.https://doi.org/10.2307/2673161 | |||
Hull R.P., Umansky P.H. (1997). An examination of gender stereotyping as an explanation for vertical job segregation in public accounting. ''Accounting, Organizations and Society'', ''22''(6), 507-528. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-3682(96)00028-1 | |||
Wong M.M.L. (1997). Women's employment status in two Japanese retail stores in Hong Kong. ''Women in Management Review'', ''12''(4), 150-157. https://doi.org/10.1108/09649429710171181 | |||
Jordan F. (1997). An occupational hazard? Sex segregation in tourism employment. ''Tourism Management'', ''18''(8), 525-534. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-5177(97)00074-5 | |||
Brown K. (1997). Evaluating equity outcomes in state public sectors: A comparison of three housing agencies. ''Australian Journal of Public Administration'', ''56''(4), 57-66. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8500.1997.tb02489.x | |||
Lee W.K.M. (1998). Gender inequality and discrimination in Singapore. ''Journal of Contemporary Asia'', ''28''(4), 484-497. https://doi.org/10.1080/00472339880000261 | |||
Egan M. (1998). Gendered integration: Social policies and the European market. ''Women and Politics'', ''19''(4), 23-52. https://doi.org/10.1300/J014v19n04_02 | |||
Marsh R.M. (1998). Gender and pay in Taiwan: Men's attitudes in 1963 and 1991. ''International Journal of Comparative Sociology'', ''39''(1), 134-137. Brill Academic Publishers.https://doi.org/10.1177/002071529803900108 | |||
Schultz V. (1998). Reconceptualizing Sexual Harassment. ''Yale Law Journal'', ''107''(6), 1683-1805. Yale Law Journal.https://doi.org/10.2307/797337 | |||
Katz E.N. (1999). Revisiting the origins of the industrial colour bar in the Witwatersrand gold mining industry, 1891 1899. ''Journal of Southern African Studies'', ''25''(1), 73-97. Carfax Publishing Company.https://doi.org/10.1080/030570799108768 | |||
Mason P.L. (1999). Male interracial wage differentials: Competing explanations. ''Cambridge Journal of Economics'', ''23''(3), 261-299. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/cje/23.3.261 | |||
Mencken F.C., Winfield I. (1999). Employer recruiting and the gender composition of jobs. ''Sociological Focus'', ''32''(2), 201-220. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380237.1999.10571135 | |||
Reskin B.F., McBrier D.B., Kmec J.A. (1999). The determinants and consequences of workplace sex and race composition. ''Annual Review of Sociology'', ''25''(), 335-361. Annual Reviews Inc..https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.soc.25.1.335 | |||
Kidd M., Goninon T. (2). Female concentration and the gender wage differential in the United Kingdom. ''Applied Economics Letters'', ''7''(5), 337-340. Routledge Journals.https://doi.org/10.1080/135048500351492 | |||
Maume Jr. D.J., Houston P. (2001). Job segregation and gender differences in work family spillover among white collar workers. ''Journal of Family and Economic Issues'', ''22''(2), 171-189. Springer New York LLC.https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016682213699 | |||
Browne I., Hewitt C., Tigges L., Green G. (2001). Why does job segregation lead to wage inequality among African Americans? Person, place, sector, or skills?. ''Social Science Research'', ''30''(3), 473-495. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1006/ssre.2001.0708 | |||
Ngo H.-Y., Foley S., Wong A., Loi R. (2003). Who Gets More of the Pie? Predictors of Perceived Gender Inequity at Work. ''Journal of Business Ethics'', ''45''(3), 227-241. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024179524538 | |||
Rudin J.P. (2003). U.S. pay equity legislation: Sheep in wolves' clothing. ''Employee Responsibilities and Rights Journal'', ''15''(4), 183-190. Springer New York.https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ERRJ.0000004057.30278.4c | |||
Guy M.E., Newman M.A. (2004). Women's jobs, men's jobs: Sex segregation and emotional labor. ''Public Administration Review'', ''64''(3), 289-298. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6210.2004.00373.x | |||
Huffman M.L., Cohen P.N. (2004). Racial Wage Inequality: Job Segregation and Devaluation Across U.S. Labor Markets. ''American Journal of Sociology'', ''109''(4), 902-936. https://doi.org/10.1086/378928 | |||
Hewitt C.M. (2004). African American concentration in jobs: The political economy of job segregation and contestation in Atlanta. ''Urban Affairs Review'', ''39''(3), 318-341. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078087403253416 | |||
Stone P., Kuperberg A. (2005). Anti discrimination vs. anti poverty? A comparison of pay equity and living wage reforms. ''Journal of Women, Politics and Policy'', ''27''(3-4), 23-39. https://doi.org/10.1300/J501v27n03_03 | |||
Kesler C. (2006). Social policy and immigrant joblessness in Britain, Germany and Sweden. ''Social Forces'', ''85''(2), 743-770. https://doi.org/10.1353/sof.2007.0013 | |||
Queneau H. (2006). Is the long term reduction in occupational sex segregation still continuing in the United States?. ''Social Science Journal'', ''43''(4), 681-688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soscij.2006.08.019 | |||
Brynin M. (2006). Gender equality through computerisation. ''European Sociological Review'', ''22''(2), 111-123. https://doi.org/10.1093/esr/jci046 | |||
DiTomaso N., Post C., Parks-Yancy R. (2007). Workforce diversity and inequality: Power, status, and numbers. ''Annual Review of Sociology'', ''33''(), 473-501. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.soc.33.040406.131805 | |||
Semyonov M., Herring C. (2007). Segregated jobs or ethnic niches?. The impact of racialized employment on earnings inequality. ''Research in Social Stratification and Mobility'', ''25''(4), 245-257. JAI Press.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rssm.2007.08.006 | |||
Ashcraft K.L. (2007). Appreciating the ‘work’ of discourse: Occupational identity and difference as organizing mechanisms in the case of commercial airline pilots. ''Discourse & Communication'', ''1''(1), 9-36. https://doi.org/10.1177/1750481307071982 | |||
Berik G., van der Meulen Rodgers Y., Seguino S. (2009). Feminist economics of inequality, development, and growth. ''Feminist Economics'', ''15''(3), 1-33. https://doi.org/10.1080/13545700903093524 | |||
Fuess S.M., Hou J.W. (2009). Rapid economic development and job segregation in Taiwan. ''Journal of Family and Economic Issues'', ''30''(2), 171-183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10834-009-9146-y | |||
Kaas L. (2009). Does equal pay legislation reduce labour market inequality?. ''Scandinavian Journal of Economics'', ''111''(1), 51-71. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9442.2008.01554.x | |||
Junor A., Hampson I., Smith M. (2009). Valuing skills: Helping mainstream gender equity in the New Zealand State sector. ''Public Policy and Administration'', ''24''(2), 195-211. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0952076708100879 | |||
Kalev A. (2009). Cracking the glass cages? Restructuring and ascriptive inequality at work. ''American Journal of Sociology'', ''114''(6), 1591-1643. https://doi.org/10.1086/597175 | |||
Williams C.L., Connell C. (201). "Looking good and sounding right": Aesthetic labor and social inequality in the retail industry. ''Work and Occupations'', ''37''(3), 349-377. https://doi.org/10.1177/0730888410373744 | |||
Duarte C.M.C., Esperança J.P., Curto J.D., Santos M.C., Carapeto M. (201). The determinants of gender pay gap in Portuguese private firms. ''Gender in Management'', ''25''(6), 438-461. https://doi.org/10.1108/17542411011069873 | |||
Guillaume C., Pochic S. (2011). The organisational nature of union careers: The touchstone of equality policies? comparing France and the UK. ''European Societies'', ''13''(4), 607-631. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616696.2011.580855 | |||
North L. (2012). ‘Blokey’ newsrooms still a battleground for female journalists. ''Australian Journalism Review'', ''34''(2), 57-70. Intellect Ltd..https://doi.org/ | |||
Kalantari B. (2012). The influence of social values and childhood socialization on occupational gender segregation and wage disparity. ''Public Personnel Management'', ''41''(2), 241-255. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/009102601204100203 | |||
Karki M., Bohara A.K. (2014). Evidence of earnings inequality based on caste in Nepal. ''Developing Economies'', ''52''(3), 262-286. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/deve.12049 | |||
Shatnawi D., Oaxaca R., Ransom M. (2014). Movin’ on up: Hierarchical occupational segmentation and gender wage gaps. ''Journal of Economic Inequality'', ''12''(3), 315-338. Springer New York LLC.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10888-013-9257-4 | |||
DiTomaso N., Parks-Yancy R. (2014). The Social Psychology of Inequality at Work: Individual, Group, and Organizational Dimensions. ''Handbooks of Sociology and Social Research'', 437-457. Springer Science and Business Media B.V..https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9002-4_18 | |||
Siebers H., van Gastel J. (2015). Why migrants earn less: in search of the factors producing the ethno migrant pay gap in a Dutch public organization. ''Work, Employment and Society'', ''29''(3), 371-391. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0950017014568138 | |||
Dobbin F., Schrage D., Kalev A. (2015). Rage against the Iron Cage: The Varied Effects of Bureaucratic Personnel Reforms on Diversity. ''American Sociological Review'', ''80''(5), 1014-1044. American Sociological Association.https://doi.org/10.1177/0003122415596416 | |||
Crowley M., Tope D., Chamberlain L.J., Hodson R. (2015). Neo taylorism at work: Occupational change in the post fordist era. ''Working in America: Continuity, Conflict, and Change in a New Economic Era'', 51-68. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315631011-16 | |||
Tomaskovic-Devey D., Hällsten M., Avent-Holt D. (2015). Where do immigrants fare worse? Modeling workplace wage gap variation with longitudinal employer employee data. ''American Journal of Sociology'', ''120''(4), 1095-1143. University of Chicago Press.https://doi.org/10.1086/679191 | |||
Cardoso A.R., Guimarães P., Portugal P. (2016). What drives the gender wage gap? A look at the role of firm and job title heterogeneity. ''Oxford Economic Papers'', ''68''(2), 506-524. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/oep/gpv069 | |||
Milkman R. (2016). Class inequalities among women. ''Sociologia del Lavoro'', 30-36. Franco Angeli Edizioni.https://doi.org/10.3280/SL2016-144003 | |||
Bonaventura L., Biondo A.E. (2016). Disclosure of sexual orientation in the USA and its consequences in the workplace. ''International Journal of Social Economics'', ''43''(11), 1115-1123. Emerald Group Publishing Ltd..https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSE-01-2015-0014 | |||
Poteyeva M., Wasileski G. (2016). Domestic violence against Albanian immigrant women in Greece: Facing patriarchy. ''Social Sciences'', ''5''(3), -. MDPI AG.https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci5030037 | |||
Wilson F.M. (2017). Organizational Behaviour and Gender. ''Organizational Behaviour and Gender'', 1-254. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315247557 | |||
Han J., Li S. (2017). Internal migration and external benefit: The impact of labor migration on the wage structure in urban China. ''China Economic Review'', ''46''(), 67-86. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2017.07.008 | |||
Boll C., Rossen A., Wolf A. (2017). The EU Gender Earnings Gap: Job Segregation and Working Time as Driving Factors. ''Jahrbucher fur Nationalokonomie und Statistik'', ''237''(5), 407-452. De Gruyter Oldenbourg.https://doi.org/10.1515/jbnst-2017-0100 | |||
Guy M. (2017). Mom Work Versus Dad Work in Local Government. ''Administration and Society'', ''49''(1), 48-64. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0095399716641989 | |||
Fodor E., Glass C. (2018). Labor market context, economic development, and family policy arrangements: Explaining the gender gap in employment in Central and Eastern Europe. ''Social Forces'', ''96''(3), 1275-1302. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/sox080 | |||
Hara H. (2018). The gender wage gap across the wage distribution in Japan: Within and between establishment effects. ''Labour Economics'', ''53''(), 213-229. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.labeco.2018.04.007 | |||
Hara H. (2018). The gender wage gap across the wage distribution in Japan: Within and between establishment effects. ''Labour Economics'', ''53''(), 213-229. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.labeco.2018.04.007 | |||
Sato K., Hashimoto Y., Owan H. (2019). Gender differences in Career. ''Journal of the Japanese and International Economies'', ''53''(), -. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjie.2019.04.001 | |||
Seguino S., Braunstein E. (2019). The Costs of Exclusion: Gender Job Segregation, Structural Change and the Labour Share of Income. ''Development and Change'', ''50''(4), 976-1008. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/dech.12462 | |||
Bueno X., Vidal-Coso E. (2019). Vulnerability of Latin American Migrant Families Headed by Women in Spain During the Great Recession: A Couple Level Analysis. ''Journal of Family Issues'', ''40''(1), 111-138. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0192513X18804584 | |||
Tverdostup M. (202). Skills utilisation and gender: Estonian case study. ''Labour Market Institutions and Productivity: Labour Utilisation in Central and Eastern Europe'', 164-187. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003009658-10 | |||
Roberts G., Schöer V. (2021). Gender based segregation in education, jobs and earnings in South Africa. ''World Development Perspectives'', ''23''(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wdp.2021.100348 | |||
Alsarhan F., Ali S., Weir D., Valax M. (2021). Impact of gender on use of wasta among human resources management practitioners. ''Thunderbird International Business Review'', ''63''(2), 131-143. Wiley-Liss Inc..https://doi.org/10.1002/tie.22186 | |||
Campero S. (2021). Hiring and Intra occupational Gender Segregation in Software Engineering. ''American Sociological Review'', ''86''(1), 60-92. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0003122420971805 | |||
Woodhams C., Trojanowski G., Wilkinson K. (2022). Merit Sticks to Men: Gender Pay Gaps and (In)equality at UK Russell Group Universities. ''Sex Roles'', ''86''(9-10), 544-558. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-022-01277-2 | |||
Latest revision as of 07:17, 16 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1][edit | edit source]
1973
United States
Definition[edit | edit source]
Job segregation refers to the practice of separating individuals into certain types of jobs based on their gender, race, age, or other protected characteristics. It is the result of discrimination and systemic biases in hiring practices and can contribute to unequal opportunities and treatment in the workplace.
Historically, women and minority groups have often been relegated to lower-paying and lower-status jobs, while men have dominated higher-paying and higher-status positions. The practice of job segregation can perpetuate stereotypes and reinforce inequalities, limiting the advancement and representation of certain groups in higher-level roles.
In many countries, laws and regulations have been established to combat job segregation and promote equal employment opportunities. These include laws like the Equal Pay Act, Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, and other antidiscrimination laws aimed at breaking down barriers and promoting diversity and inclusion in the workforce.
While progress has been made over the years, job segregation still persists in many industries and professions. Efforts to address this issue involve promoting diversity and inclusion in recruitment, providing equal opportunities for training and advancement, and challenging stereotypes and biases that contribute to job segregation.
Overall, job segregation is a detrimental practice that limits individual potential and hinders social progress. Creating inclusive workplaces where individuals of all backgrounds have equal opportunities for employment and advancement is crucial for creating a fair and equitable society.
See also[edit | edit source]
Related segregation forms[edit | edit source]
Job segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
occupational segregation, gender segregation, sex segregation, occupational gender segregation, racial segregation, social segregation, black residential segregation, black segregation, residential segregation, labor market segregation, horizontal segregation
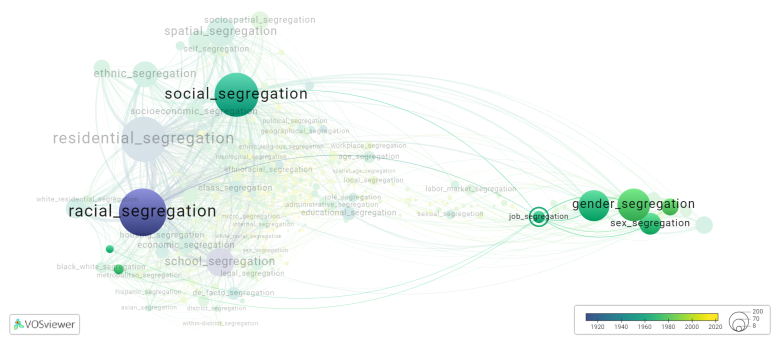
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References[edit | edit source]
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Job segregation appears in the following literature[edit | edit source]
Marshall R. (1963). Some factors influencing the upgrading of negroes in the southern petroleu \1 refining industry. Social Forces, 42(2), 186-195. https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/42.2.186
Stevenson M. (1973). Women's Wages and Job Segregation. Politics & Society, 4(1), 83-96. https://doi.org/10.1177/003232927300400104
Wisniewski S.C. (1982). Achieving equal pay for comparable worth through arbitration.. Employee relations law journal, 8(2), 236-255. https://doi.org/
Stahura J.M. (1983). Determinants of Change in the Distribution of Blacks across Suburbs. Sociological Quarterly, 24(3), 421-433. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1533-8525.1983.tb00711.x
Reskin B.F. (1988). Bringing the men back in: Sex Differentiation and the Devaluation of Women's Work. Gender & Society, 2(1), 58-81. https://doi.org/10.1177/089124388002001005
Hensman R. (1988). The gender divisions of labour in manufacturing industry a case study in india. South Asia Research, 8(2), 133-153. https://doi.org/10.1177/026272808800800203
Williams R.M., Smith P.R. (199). What else do unions do?: Race and gender in local 35. The Review of Black Political Economy, 18(3), 59-74. Springer-Verlag.https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02717875
Hou J.W. (1991). Wage comparison by gender and the effect of job segregation: The case of Taiwan. China Economic Review, 2(2), 195-214. https://doi.org/10.1016/1043-951X(91)90004-R
Morgan G., Knights D. (1991). Gendering jobs: Corporate strategy, managerial control and the dynamics of job segregation. Work Employment & Society, 5(2), 181-200. https://doi.org/10.1177/0950017091005002003
Grand C. (1991). Explaining the Male Female Wage Gap: Job Segregation and Solidarity Wage Bargaining in Sweden. Acta Sociologica, 34(4), 261-277. https://doi.org/10.1177/000169939103400402
Hakim C. (1991). Grateful slaves and self made women: Fact and fantasy in women's work orientations. European Sociological Review, 7(2), 101-121. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.esr.a036590
Devine F. (1993). Gender segregation and labour supply: On ‘choosing’ gender atypical jobs. British Journal of Education & Work, 6(3), 61-74. https://doi.org/10.1080/0269000930060304
Tanski J.M. (1994). The impact of crisis, stabilization and structural adjustment on women in Lima, Peru. World Development, 22(11), 1627-1642. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-750X(94)00073-5
Kenney S.J. (1994). Who Is Protected? What’s Wrong ith Exclusionary Policies. Women and Politics, 13(3-4), 153-173. https://doi.org/10.1300/J014v13n03_10
Core F. (1994). Women and the restructuring of employment. OECD Observer, 186(), 5-12. https://doi.org/
Hutton S. (1994). Men's and women's incomes: evidence from survey data. Journal of Social Policy, 23(1), 21-40. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0047279400021309
Kulis S.S., Shaw H.E. (1996). Racial segregation among postsecondary workers. Social Forces, 75(2), 575-591. University of North Carolina Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/75.2.575
Kulis S. (1997). Gender segregation among college and university employees. Sociology of Education, 70(2), 151-173. American Sociological Association.https://doi.org/10.2307/2673161
Hull R.P., Umansky P.H. (1997). An examination of gender stereotyping as an explanation for vertical job segregation in public accounting. Accounting, Organizations and Society, 22(6), 507-528. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0361-3682(96)00028-1
Wong M.M.L. (1997). Women's employment status in two Japanese retail stores in Hong Kong. Women in Management Review, 12(4), 150-157. https://doi.org/10.1108/09649429710171181
Jordan F. (1997). An occupational hazard? Sex segregation in tourism employment. Tourism Management, 18(8), 525-534. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-5177(97)00074-5
Brown K. (1997). Evaluating equity outcomes in state public sectors: A comparison of three housing agencies. Australian Journal of Public Administration, 56(4), 57-66. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8500.1997.tb02489.x
Lee W.K.M. (1998). Gender inequality and discrimination in Singapore. Journal of Contemporary Asia, 28(4), 484-497. https://doi.org/10.1080/00472339880000261
Egan M. (1998). Gendered integration: Social policies and the European market. Women and Politics, 19(4), 23-52. https://doi.org/10.1300/J014v19n04_02
Marsh R.M. (1998). Gender and pay in Taiwan: Men's attitudes in 1963 and 1991. International Journal of Comparative Sociology, 39(1), 134-137. Brill Academic Publishers.https://doi.org/10.1177/002071529803900108
Schultz V. (1998). Reconceptualizing Sexual Harassment. Yale Law Journal, 107(6), 1683-1805. Yale Law Journal.https://doi.org/10.2307/797337
Katz E.N. (1999). Revisiting the origins of the industrial colour bar in the Witwatersrand gold mining industry, 1891 1899. Journal of Southern African Studies, 25(1), 73-97. Carfax Publishing Company.https://doi.org/10.1080/030570799108768
Mason P.L. (1999). Male interracial wage differentials: Competing explanations. Cambridge Journal of Economics, 23(3), 261-299. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/cje/23.3.261
Mencken F.C., Winfield I. (1999). Employer recruiting and the gender composition of jobs. Sociological Focus, 32(2), 201-220. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380237.1999.10571135
Reskin B.F., McBrier D.B., Kmec J.A. (1999). The determinants and consequences of workplace sex and race composition. Annual Review of Sociology, 25(), 335-361. Annual Reviews Inc..https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.soc.25.1.335
Kidd M., Goninon T. (2). Female concentration and the gender wage differential in the United Kingdom. Applied Economics Letters, 7(5), 337-340. Routledge Journals.https://doi.org/10.1080/135048500351492
Maume Jr. D.J., Houston P. (2001). Job segregation and gender differences in work family spillover among white collar workers. Journal of Family and Economic Issues, 22(2), 171-189. Springer New York LLC.https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016682213699
Browne I., Hewitt C., Tigges L., Green G. (2001). Why does job segregation lead to wage inequality among African Americans? Person, place, sector, or skills?. Social Science Research, 30(3), 473-495. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1006/ssre.2001.0708
Ngo H.-Y., Foley S., Wong A., Loi R. (2003). Who Gets More of the Pie? Predictors of Perceived Gender Inequity at Work. Journal of Business Ethics, 45(3), 227-241. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024179524538
Rudin J.P. (2003). U.S. pay equity legislation: Sheep in wolves' clothing. Employee Responsibilities and Rights Journal, 15(4), 183-190. Springer New York.https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ERRJ.0000004057.30278.4c
Guy M.E., Newman M.A. (2004). Women's jobs, men's jobs: Sex segregation and emotional labor. Public Administration Review, 64(3), 289-298. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6210.2004.00373.x
Huffman M.L., Cohen P.N. (2004). Racial Wage Inequality: Job Segregation and Devaluation Across U.S. Labor Markets. American Journal of Sociology, 109(4), 902-936. https://doi.org/10.1086/378928
Hewitt C.M. (2004). African American concentration in jobs: The political economy of job segregation and contestation in Atlanta. Urban Affairs Review, 39(3), 318-341. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078087403253416
Stone P., Kuperberg A. (2005). Anti discrimination vs. anti poverty? A comparison of pay equity and living wage reforms. Journal of Women, Politics and Policy, 27(3-4), 23-39. https://doi.org/10.1300/J501v27n03_03
Kesler C. (2006). Social policy and immigrant joblessness in Britain, Germany and Sweden. Social Forces, 85(2), 743-770. https://doi.org/10.1353/sof.2007.0013
Queneau H. (2006). Is the long term reduction in occupational sex segregation still continuing in the United States?. Social Science Journal, 43(4), 681-688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soscij.2006.08.019
Brynin M. (2006). Gender equality through computerisation. European Sociological Review, 22(2), 111-123. https://doi.org/10.1093/esr/jci046
DiTomaso N., Post C., Parks-Yancy R. (2007). Workforce diversity and inequality: Power, status, and numbers. Annual Review of Sociology, 33(), 473-501. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.soc.33.040406.131805
Semyonov M., Herring C. (2007). Segregated jobs or ethnic niches?. The impact of racialized employment on earnings inequality. Research in Social Stratification and Mobility, 25(4), 245-257. JAI Press.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rssm.2007.08.006
Ashcraft K.L. (2007). Appreciating the ‘work’ of discourse: Occupational identity and difference as organizing mechanisms in the case of commercial airline pilots. Discourse & Communication, 1(1), 9-36. https://doi.org/10.1177/1750481307071982
Berik G., van der Meulen Rodgers Y., Seguino S. (2009). Feminist economics of inequality, development, and growth. Feminist Economics, 15(3), 1-33. https://doi.org/10.1080/13545700903093524
Fuess S.M., Hou J.W. (2009). Rapid economic development and job segregation in Taiwan. Journal of Family and Economic Issues, 30(2), 171-183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10834-009-9146-y
Kaas L. (2009). Does equal pay legislation reduce labour market inequality?. Scandinavian Journal of Economics, 111(1), 51-71. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9442.2008.01554.x
Junor A., Hampson I., Smith M. (2009). Valuing skills: Helping mainstream gender equity in the New Zealand State sector. Public Policy and Administration, 24(2), 195-211. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0952076708100879
Kalev A. (2009). Cracking the glass cages? Restructuring and ascriptive inequality at work. American Journal of Sociology, 114(6), 1591-1643. https://doi.org/10.1086/597175
Williams C.L., Connell C. (201). "Looking good and sounding right": Aesthetic labor and social inequality in the retail industry. Work and Occupations, 37(3), 349-377. https://doi.org/10.1177/0730888410373744
Duarte C.M.C., Esperança J.P., Curto J.D., Santos M.C., Carapeto M. (201). The determinants of gender pay gap in Portuguese private firms. Gender in Management, 25(6), 438-461. https://doi.org/10.1108/17542411011069873
Guillaume C., Pochic S. (2011). The organisational nature of union careers: The touchstone of equality policies? comparing France and the UK. European Societies, 13(4), 607-631. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616696.2011.580855
North L. (2012). ‘Blokey’ newsrooms still a battleground for female journalists. Australian Journalism Review, 34(2), 57-70. Intellect Ltd..https://doi.org/
Kalantari B. (2012). The influence of social values and childhood socialization on occupational gender segregation and wage disparity. Public Personnel Management, 41(2), 241-255. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/009102601204100203
Karki M., Bohara A.K. (2014). Evidence of earnings inequality based on caste in Nepal. Developing Economies, 52(3), 262-286. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/deve.12049
Shatnawi D., Oaxaca R., Ransom M. (2014). Movin’ on up: Hierarchical occupational segmentation and gender wage gaps. Journal of Economic Inequality, 12(3), 315-338. Springer New York LLC.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10888-013-9257-4
DiTomaso N., Parks-Yancy R. (2014). The Social Psychology of Inequality at Work: Individual, Group, and Organizational Dimensions. Handbooks of Sociology and Social Research, 437-457. Springer Science and Business Media B.V..https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9002-4_18
Siebers H., van Gastel J. (2015). Why migrants earn less: in search of the factors producing the ethno migrant pay gap in a Dutch public organization. Work, Employment and Society, 29(3), 371-391. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0950017014568138
Dobbin F., Schrage D., Kalev A. (2015). Rage against the Iron Cage: The Varied Effects of Bureaucratic Personnel Reforms on Diversity. American Sociological Review, 80(5), 1014-1044. American Sociological Association.https://doi.org/10.1177/0003122415596416
Crowley M., Tope D., Chamberlain L.J., Hodson R. (2015). Neo taylorism at work: Occupational change in the post fordist era. Working in America: Continuity, Conflict, and Change in a New Economic Era, 51-68. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315631011-16
Tomaskovic-Devey D., Hällsten M., Avent-Holt D. (2015). Where do immigrants fare worse? Modeling workplace wage gap variation with longitudinal employer employee data. American Journal of Sociology, 120(4), 1095-1143. University of Chicago Press.https://doi.org/10.1086/679191
Cardoso A.R., Guimarães P., Portugal P. (2016). What drives the gender wage gap? A look at the role of firm and job title heterogeneity. Oxford Economic Papers, 68(2), 506-524. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/oep/gpv069
Milkman R. (2016). Class inequalities among women. Sociologia del Lavoro, 30-36. Franco Angeli Edizioni.https://doi.org/10.3280/SL2016-144003
Bonaventura L., Biondo A.E. (2016). Disclosure of sexual orientation in the USA and its consequences in the workplace. International Journal of Social Economics, 43(11), 1115-1123. Emerald Group Publishing Ltd..https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSE-01-2015-0014
Poteyeva M., Wasileski G. (2016). Domestic violence against Albanian immigrant women in Greece: Facing patriarchy. Social Sciences, 5(3), -. MDPI AG.https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci5030037
Wilson F.M. (2017). Organizational Behaviour and Gender. Organizational Behaviour and Gender, 1-254. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315247557
Han J., Li S. (2017). Internal migration and external benefit: The impact of labor migration on the wage structure in urban China. China Economic Review, 46(), 67-86. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2017.07.008
Boll C., Rossen A., Wolf A. (2017). The EU Gender Earnings Gap: Job Segregation and Working Time as Driving Factors. Jahrbucher fur Nationalokonomie und Statistik, 237(5), 407-452. De Gruyter Oldenbourg.https://doi.org/10.1515/jbnst-2017-0100
Guy M. (2017). Mom Work Versus Dad Work in Local Government. Administration and Society, 49(1), 48-64. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0095399716641989
Fodor E., Glass C. (2018). Labor market context, economic development, and family policy arrangements: Explaining the gender gap in employment in Central and Eastern Europe. Social Forces, 96(3), 1275-1302. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/sox080
Hara H. (2018). The gender wage gap across the wage distribution in Japan: Within and between establishment effects. Labour Economics, 53(), 213-229. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.labeco.2018.04.007
Hara H. (2018). The gender wage gap across the wage distribution in Japan: Within and between establishment effects. Labour Economics, 53(), 213-229. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.labeco.2018.04.007
Sato K., Hashimoto Y., Owan H. (2019). Gender differences in Career. Journal of the Japanese and International Economies, 53(), -. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjie.2019.04.001
Seguino S., Braunstein E. (2019). The Costs of Exclusion: Gender Job Segregation, Structural Change and the Labour Share of Income. Development and Change, 50(4), 976-1008. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/dech.12462
Bueno X., Vidal-Coso E. (2019). Vulnerability of Latin American Migrant Families Headed by Women in Spain During the Great Recession: A Couple Level Analysis. Journal of Family Issues, 40(1), 111-138. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0192513X18804584
Tverdostup M. (202). Skills utilisation and gender: Estonian case study. Labour Market Institutions and Productivity: Labour Utilisation in Central and Eastern Europe, 164-187. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003009658-10
Roberts G., Schöer V. (2021). Gender based segregation in education, jobs and earnings in South Africa. World Development Perspectives, 23(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wdp.2021.100348
Alsarhan F., Ali S., Weir D., Valax M. (2021). Impact of gender on use of wasta among human resources management practitioners. Thunderbird International Business Review, 63(2), 131-143. Wiley-Liss Inc..https://doi.org/10.1002/tie.22186
Campero S. (2021). Hiring and Intra occupational Gender Segregation in Software Engineering. American Sociological Review, 86(1), 60-92. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0003122420971805
Woodhams C., Trojanowski G., Wilkinson K. (2022). Merit Sticks to Men: Gender Pay Gaps and (In)equality at UK Russell Group Universities. Sex Roles, 86(9-10), 544-558. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-022-01277-2
