Neighborhood segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Neighborhood segregation refers to the separation of people from different races, ethnicities, or socioeconomic backgrounds into different neighborhoods. This segregation can result from various factors such as housing discrimination, economic inequality, and historical patterns of residential segregation. Neighborhood segregation can have negative impacts on communities, leading to disparities in access to quality education, healthcare, employment opportunities, and other resources. Efforts to address neighborhood segregation often involve policies and initiatives aimed at promoting diversity, inclusivity, and equitable access to housing and services. | Neighborhood segregation refers to the separation of people from different races, ethnicities, or socioeconomic backgrounds into different neighborhoods. This segregation can result from various factors such as housing discrimination, economic inequality, and historical patterns of residential segregation. Neighborhood segregation can have negative impacts on communities, leading to disparities in access to quality education, healthcare, employment opportunities, and other resources. Efforts to address neighborhood segregation often involve policies and initiatives aimed at promoting diversity, inclusivity, and equitable access to housing and services. | ||
===== Synonyms ===== | ===== Synonyms ===== | ||
The following terms are synonymous with: | The following terms are synonymous with neighborhood segregation: | ||
neighborhood level segregation; neighborhood scale segregation; neighbourhood segregation; neighbourhood's segregation. | neighborhood level segregation; neighborhood scale segregation; neighbourhood segregation; neighbourhood's segregation. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
Neighborhood segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms: | Neighborhood segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms: | ||
[[ | [[racial segregation]], [[residential segregation]], [[social segregation]], [[school segregation]], [[racial residential segregation]], [[ethnic segregation]], [[spatial segregation]], [[neighborhood residential segregation]], [[housing segregation]], [[educational segregation]], [[white residential segregation]], [[economic segregation]], [[black residential segregation]], [[urban segregation]] | ||
[[File:neighborhood_segregation.png|780x780px]] | [[File:neighborhood_segregation.png|780x780px]] | ||
This visualization is based on the study [[Segregation_Wiki:About| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of | For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | ||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 07:17, 16 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1][edit | edit source]
1966
United States
Definition[edit | edit source]
Neighborhood segregation refers to the separation of people from different races, ethnicities, or socioeconomic backgrounds into different neighborhoods. This segregation can result from various factors such as housing discrimination, economic inequality, and historical patterns of residential segregation. Neighborhood segregation can have negative impacts on communities, leading to disparities in access to quality education, healthcare, employment opportunities, and other resources. Efforts to address neighborhood segregation often involve policies and initiatives aimed at promoting diversity, inclusivity, and equitable access to housing and services.
Synonyms[edit | edit source]
The following terms are synonymous with neighborhood segregation:
neighborhood level segregation; neighborhood scale segregation; neighbourhood segregation; neighbourhood's segregation.
References and literature addressing this segregation form under these synonymous terms can be found below.
See also[edit | edit source]
Related segregation forms[edit | edit source]
Neighborhood segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
racial segregation, residential segregation, social segregation, school segregation, racial residential segregation, ethnic segregation, spatial segregation, neighborhood residential segregation, housing segregation, educational segregation, white residential segregation, economic segregation, black residential segregation, urban segregation
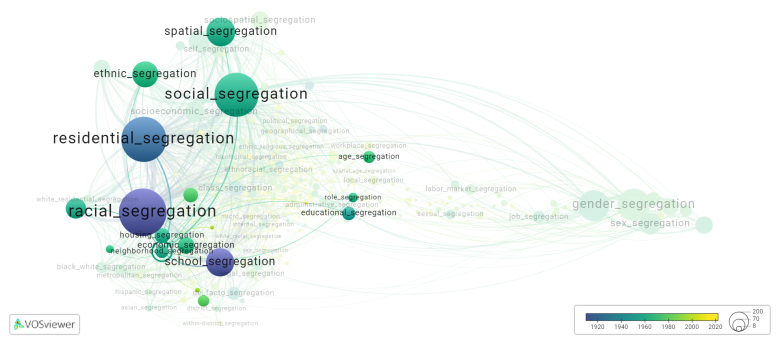
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References[edit | edit source]
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Neighborhood segregation appears in the following literature[edit | edit source]
Ross J.M., Crawford T., Pettigrew T. (1966). Negro neighbors banned in Boston The current racial skirmish concerns school integration, but Boston's problem is neighborhood segregation. Trans-action, 3(6), 13-18. Springer-Verlag.https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02804393
Orfield G. (1979). School segregation and housing policy: The role of local and federal governments in neighborhood segregation. Equity and Excellence in Education, 17(3-4), 48-53. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020486790170305
Goodman A.C. (1985). A NOTE ON NEIGHBORHOOD SIZE AND THE MEASUREMENT OF SEGREGATION INDICES. Journal of Regional Science, 25(3), 471-476. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9787.1985.tb00315.x
James F.J. (1986). A New Generalized “Exposure Based” Segregation Index: Demonstration in Denver and Houston. Sociological Methods & Research, 14(3), 301-316. https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124186014003005
Goldberg D.T. (1998). The new segregation. Race and Society, 1(1), 15-32. Elsevier BV.https://doi.org/10.1016/S1090-9524(99)80184-3
Wyly E.K. (1999). Continuity and change in the restless urban landscape. Economic Geography, 75(4), 309-338. Clark University.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1944-8287.1999.tb00124.x
Wasserman H., Yohe G. (2001). Segregation and the Provision of Spatially Defined Local Public Goods. American Economist, 45(2), 13-24. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/056943450104500202
Batten D.F. (2001). Complex landscapes of spatial interaction. Annals of Regional Science, 35(1), 81-111. Springer Verlag.https://doi.org/10.1007/s001680000032
Dawkins C.J. (2005). Tiebout choice and residential segregation by race in US metropolitan areas, 1980 2000. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 35(6), 734-755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2005.01.002
Keels M., Duncan G.J., DeLuca S., Mendenhall R., Rusenbaum J. (2005). Fifteen years later: Can residential mobility programs provide a long term escape from neighborhood segregation, crime, and poverty?. Demography, 42(1), 51-73. Duke University Press.https://doi.org/10.1353/dem.2005.0005
Kray C.A. (2006). Resistance to what? How?: Stalled social movements in Cancun. City and Society, 18(1), 66-89. https://doi.org/10.1525/city.2006.18.1.66
Pancs R., Vriend N.J. (2007). Schelling's spatial proximity model of segregation revisited. Journal of Public Economics, 91(1-2), 1-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2006.03.008
Card D., Rothstein J. (2007). Racial segregation and the black white test score gap. Journal of Public Economics, 91(11-12), 2158-2184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2007.03.006
Lee M.-A., Ferraro K.F. (2007). Neighborhood residential segregation and physical health among hispanic Americans: Good, bad, or benign?. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 48(2), 131-148. American Sociological Association.https://doi.org/10.1177/002214650704800203
Ellis M., Holloway S.R., Wright R., East M. (2007). The effects of mixed race households on residential segregation. Urban Geography, 28(6), 554-577. https://doi.org/10.2747/0272-3638.28.6.554
Kleit R.G. (2008). Neighborhood segregation, personal networks, and access to social resources. Segregation: The Rising Costs for America, 237-260. Routledge Taylor & Francis Group.https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203895023
Vigdor J.L., Ludwig J. (2008). Segregation and the test score gap. Steady Gains and Stalled Progress: Inequality and The Black-White Test Score Gap, 181-211. Russell Sage Foundation.https://doi.org/
Wong D.W.S. (2008). A local multidimensional approach to evaluate changes in segregation. Urban Geography, 29(5), 455-472. https://doi.org/10.2747/0272-3638.29.5.455
Lee M.-A. (2009). Neighborhood residential segregation and mental health: A multilevel analysis on Hispanic Americans in Chicago. Social Science and Medicine, 68(11), 1975-1984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2009.02.040
Müller T., Ramirez J. (2009). Wage inequality and segregation between native and immigrant workers in Switzerland: Evidence using matched employee employer data. Research on Economic Inequality, 17(), 205-243. https://doi.org/10.1108/S1049-2585(2009)0000017014
Oyserman D., Yoon K.-I. (2009). Neighborhood Effects on Racial Ethnic Identity: The Undermining Role of Segregation. Race and Social Problems, 1(2), 67-76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12552-009-9007-1
Berg N., Hoffrage U., Abramczuk K. (201). Fast acceptance by common experience: FACE recognition in schelling's model of neighborhood segregation. Judgment and Decision Making, 5(5), 391-410. https://doi.org/
Spinner-Halev J. (201). The trouble with diversity. Critical Urban Studies: New Directions, 107-120. State University of New York Press.https://doi.org/
Margai F.M. (201). Racial/ethnic disparities in health and health care in the U.S.: A geographic overview. Race, Ethnicity, and Place in a Changing America, 379-392. State University of New York Press.https://doi.org/
Parisi D., Lichter D.T., Taquino M.C. (2011). Multi scale residential segregation: Black exceptionalism and America's changing color line. Social Forces, 89(3), 829-852. https://doi.org/10.1353/sof.2011.0013
Clark W. (2011). Residential Segregation and Education. International Encyclopedia of Housing and Home, 100-104. Elsevier.https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-047163-1.00035-7
Bennett P.R. (2011). The relationship between neighborhood racial concentration and verbal ability: An investigation using the institutional resources model. Social Science Research, 40(4), 1124-1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssresearch.2011.04.001
Manley D., van Ham M. (2011). Choice based letting, ethnicity and segregation in England. Urban Studies, 48(14), 3125-3143. https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098010394685
de Bodman F., Bennett P.R. (2011). Mr. secretary, tear down this wall: Can and Should the Federal Government Use Affirmative Action to Promote Residential Integration?. Du Bois Review, 8(2), 441-466. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742058X11000427
Goyette K.A., Farrie D., Freely J. (2012). This school's gone downhill: Racial change and perceived school quality among whites. Social Problems, 59(2), 155-176. https://doi.org/10.1525/sp.2012.59.2.155
Clark W.A.V., Maas R. (2012). Schools, Neighborhoods and Selection: Outcomes Across Metropolitan Los Angeles. Population Research and Policy Review, 31(3), 339-360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11113-012-9234-9
Ellis M., Holloway S.R., Wright R., Fowler C.S. (2012). Agents of Change: Mixed Race Households and the Dynamics of Neighborhood Segregation in the United States. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 102(3), 549-570. https://doi.org/10.1080/00045608.2011.627057
Hällsten M., Szulkin R., Sarnecki J. (2013). Crime as a Price of Inequality?. British Journal of Criminology, 53(3), 456-481. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjc/azt005
Arnold E. (2013). Simulation models of the evolution of cooperation as proofs of logical possibilities. How useful are they?. Etica e Politica, 15(2), 101-138. https://doi.org/
Berg N., Abramczuk K., Hoffrage U. (2013). Fast Acceptance by Common Experience: Augmenting Schelling's Neighborhood Segregation Model With FACE Recognition. Simple Heuristics in a Social World, -. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195388435.003.0008
Wright R., Holloway S., Ellis M. (2013). Gender and the Neighborhood Location of Mixed Race Couples. Demography, 50(2), 393-420. Duke University Press.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-012-0158-0
Bell J. (2013). Hate thy neighbor: Move In violence and the persistence of racial segregation in American housing. Hate Thy Neighbor: Move-In Violence and the Persistence of Racial Segregation in American Housing, 1-249. New York University Press.https://doi.org/
Arnold E. (2014). What's wrong with social simulations?. Monist, 97(3), 359-377. Hegeler Institute.https://doi.org/10.5840/monist201497323
Yi S.S., Ruff R.R., Jung M., Waddell E.N. (2014). Racial/ethnic residential segregation, neighborhood poverty and urinary biomarkers of diet in New York City adults. Social Science and Medicine, 122(), 122-129. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2014.10.030
Lloyd C.D., Catney G., Shuttleworth I.G. (2014). Measuring neighbourhood segregation using spatial interaction data. Social-Spatial Segregation: Concepts, Processes and Outcomes, 65-90. Policy Press.https://doi.org/
Johnson O., Jr. (2014). Still separate, still unequal: The relation of segregation in neighborhoods and schools to education inequality. Journal of Negro Education, 83(3), 199-215. Howard University.https://doi.org/10.7709/jnegroeducation.83.3.0199
Bruch E.E. (2014). How population structure shapes neighborhood segregation. American Journal of Sociology, 119(5), 1221-1278. University of Chicago Press.https://doi.org/10.1086/675411
Ouazad A. (2015). Blockbusting: Brokers and the dynamics of segregation. Journal of Economic Theory, 157(), 811-841. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jet.2015.02.006
Brasington D.M., Hite D., Jauregui A. (2015). House price impacts of racial, income, education, and age neighborhood segregation. Journal of Regional Science, 55(3), 442-467. https://doi.org/10.1111/jors.12173
Brasington D.M., Hite D., Jauregui A. (2015). House price impacts of racial, income, education, and age neighborhood segregation. Journal of Regional Science, 55(3), 442-467. https://doi.org/10.1111/jors.12173
Boen C. (2016). The role of socioeconomic factors in Black White health inequities across the life course: Point in time measures, long term exposures, and differential health returns. Social Science and Medicine, 170(), 63-76. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2016.10.008
Ruiz J.M., Hamann H.A., Mehl M.R., O’Connor M.-F. (2016). The Hispanic health paradox: From epidemiological phenomenon to contribution opportunities for psychological science. Group Processes and Intergroup Relations, 19(4), 462-476. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/1368430216638540
Kidron A. (2016). Separatism, coexistence and the landscape: Jews and Palestinian Arabs in mandatory Haifa. Middle Eastern Studies, 52(1), 79-101. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/00263206.2015.1081177
Spamann H. (2016). The U.S. crime puzzle: A comparative perspective on U.S. crime and punishment. American Law and Economics Review, 18(1), 33-87. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/aler/ahv015
Böhlmark A., Holmlund H., Lindahl M. (2016). Parental choice, neighbourhood segregation or cream skimming? An analysis of school segregation after a generalized choice reform. Journal of Population Economics, 29(4), 1155-1190. Springer New York LLC.https://doi.org/10.1007/s00148-016-0595-y
Owens A., Reardon S.F., Jencks C. (2016). Income Segregation Between Schools and School Districts. American Educational Research Journal, 53(4), 1159-1197. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831216652722
Ellis M., Holloway S.R., Wright R., Fowler C.S. (2016). Agents of change: Mixed race households and the dynamics of neighborhood segregation in the United States. Handbook of Applied System Science, 486-511. Taylor and Francis Inc..https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315748771
Trevizo D., Lopez M.J. (2016). Neighborhood Segregation and Business Outcomes: Mexican Immigrant Entrepreneurs in Los Angeles County. Sociological Perspectives, 59(3), 668-693. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0731121416629992
Moody H.A., Darden J.T., Pigozzi B.W. (2016). The Relationship of Neighborhood Socioeconomic Differences and Racial Residential Segregation to Childhood Blood Lead Levels in Metropolitan Detroit. Journal of Urban Health, 93(5), 820-839. Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11524-016-0071-8
Walks A. (2016). Homeownership, Asset based Welfare and the Neighbourhood Segregation of Wealth. Housing Studies, 31(7), 755-784. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/02673037.2015.1132685
Hermansen A.S. (2016). Moving Up or Falling Behind? Intergenerational Socioeconomic Transmission among Children of Immigrants in Norway. European Sociological Review, 32(5), 675-689. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/esr/jcw024
Owens A. (2016). Inequality in Children’s Contexts: Income Segregation of Households with and without Children. American Sociological Review, 81(3), 549-574. American Sociological Association.https://doi.org/10.1177/0003122416642430
Fesselmeyer E., Seah K.Y. (2017). Neighborhood segregation and black entrepreneurship. Economics Letters, 154(), 88-91. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econlet.2017.02.025
Roda A. (2017). ‘More [Time] is better or less is more?’ Neoliberal influences on teaching and learning time. Journal of Education Policy, 32(3), 303-321. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/02680939.2016.1255917
Mayer T. (2017). School choice and the urban neighbourhood: Segregation processes in the german primary sector with special reference to private schools. Private Schools and School Choice in Compulsory Education: Global Change and National Challenge, 153-175. Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-17104-9_10
Owens A. (2017). Racial residential segregation of school age children and adults: The role of schooling as a segregating force. RSF, 3(2), 63-80. Russell Sage Foundation.https://doi.org/10.7758/rsf.2017.3.2.03
Johnston R., Harris R., Jones K., Manley D. (2017). Segregation at school and at home: An English exploration. BELGEO, -. Societe Belge de Geographie.https://doi.org/10.4000/belgeo.18730
Larson S.J. (2018). Examining the Efficacy of Title VI Social Equity Analysis: A Comparative Case Study of Transit Access and Neighborhood Segregation Outcomes Over Time. Public Integrity, 20(4), 344-357. Taylor and Francis Ltd..https://doi.org/10.1080/10999922.2018.1441595
Heilmann K. (2018). Transit access and neighborhood segregation. Evidence from the Dallas light rail system. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 73(), 237-250. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2018.10.007
McCutcheon R., Bloomfield M.A.P., Dahoun T., Quinlan M., Terbeck S., Mehta M., Howes O. (2018). Amygdala reactivity in ethnic minorities and its relationship to the social environment: An fMRI study. Psychological Medicine, 48(12), 1985-1992. Cambridge University Press.https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291717003506
Frankenberg E. (2018). Preferences, Proximity, and Controlled Choice: Examining Families’ School Choices and Enrollment Decisions in Louisville, Kentucky. Peabody Journal of Education, 93(4), 378-394. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/0161956X.2018.1488392
Griswold M.K., Crawford S.L., Perry D.J., Person S.D., Rosenberg L., Cozier Y.C., Palmer J.R. (2018). Experiences of Racism and Breastfeeding Initiation and Duration Among First Time Mothers of the Black Women’s Health Study. Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities, 5(6), 1180-1191. Springer International Publishing.https://doi.org/10.1007/s40615-018-0465-2
Talen E. (2018). The relentless link between neighbourhoods and segregation: What are the alternatives?. Town Planning Review, 89(5), 443-462. Liverpool University Press.https://doi.org/10.3828/tpr.2018.29
Doebler S., McAreavey R., Shortall S. (2018). Is racism the new sectarianism? Negativity towards immigrants and ethnic minorities in Northern Ireland from 2004 to 2015. Ethnic and Racial Studies, 41(14), 2426-2444. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/01419870.2017.1392027
Müller T.S., Grund T.U., Koskinen J.H. (2018). Residential Segregation and 'Ethnic Flight' vs. 'Ethnic Avoidance' in Sweden. European Sociological Review, 34(3), 268-285. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/esr/jcy010
Bruch E., Swait J. (2019). Choice Set Formation in Residential Mobility and Its Implications for Segregation Dynamics. Demography, 56(5), 1665-1692. Springer Science and Business Media, LLC.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-019-00810-5
Nielsen M.M., Hennerdal P. (2019). Segregation of Residents with Tertiary Education in Sweden from 1990 to 2012. Professional Geographer, 71(2), 301-314. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/00330124.2018.1518719
Phillips II G., McCuskey D.J., Felt D., Raman A.B., Hayford C.S., Pickett J., Shenkman J., Lindeman P.T., Mustanski B. (202). Geospatial perspectives on health: The PrEP4Love campaign and the role of local context in health promotion messaging. Social Science and Medicine, 265(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.113497
Gutiérrez G., Jerrim J., Torres R. (202). School Segregation Across the World: Has Any Progress Been Made in Reducing the Separation of the Rich from the Poor?. Journal of Economic Inequality, 18(2), 157-179. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10888-019-09437-3
Berrelleza E. (202). Exclusion in Upscaling Institutions: The Reproduction of Neighborhood Segregation in an Urban Church. City and Community, 19(3), 747-770. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/cico.12474
Lee H., Caldwell J.T., Maene C., Cagney K.A., Saunders M.R. (202). Racial/Ethnic Inequities in Access to High Quality Dialysis Treatment in Chicago: Does Neighborhood Racial/Ethnic Composition Matter?. Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities, 7(5), 854-864. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s40615-020-00708-8
Owens A. (202). Unequal Opportunity: School and Neighborhood Segregation in the USA. Race and Social Problems, 12(1), 29-41. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s12552-019-09274-z
Karlsson H. (202). Is discrimination a driving force behind the over representation of children with an immigrant background in Swedish out of home care? A quantitative study from Stockholm City; [ Driver diskriminering överrepresentationen av barn med invandrarbakgrund i svensk dygnet runt vård? En kvantitativ studie från Stockholm stad.]. European Journal of Social Work, 1-13. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/13691457.2020.1793113
Jiang G. (2021). Schelling's model revisited: From segregation to integration. Economics Letters, 205(), -. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econlet.2021.109953
Heblich S., Trew A., Zylberberg Y. (2021). East side story: Historical pollution and persistent neighborhood sorting. Journal of Political Economy, 129(5), 1508-1552. University of Chicago Press.https://doi.org/10.1086/713101
Beltran A., Chong A., Montoya M. (2021). Socio economic level, neighborhood segregation and determinants of reciprocity: evidence using representative artefactual data from Latin American cities. Journal of Economic Policy Reform, -. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/17487870.2021.1962716
Mann B., Rogers A. (2021). Segregation Now, Segregation Tomorrow, Segregation Forever? Racial and Economic Isolation and Dissimilarity in Rural Black Belt Schools in Alabama*. Rural Sociology, 86(3), 523-558. Rural Sociological Society.https://doi.org/10.1111/ruso.12384
Rich P., Candipan J., Owens A. (2021). Segregated neighborhoods, segregated schools: Do charters break a stubborn link?. Demography, 58(2), 471-498. Duke University Press.https://doi.org/10.1215/00703370-9000820
Persad G. (2021). Allocating medicine fairly in an unfair pandemic. University of Illinois Law Review, 2021(3), 1085-1134. University of Illinois College of Law.https://doi.org/
Trochmann M. (2021). Identities, Intersectionality, and Otherness: The Social Constructions of Deservedness in American Housing Policy. Administrative Theory and Praxis, 43(1), 97-116. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/10841806.2019.1700456
Lin J., Rauch F. (2022). What future for history dependence in spatial economics?. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 94(), -. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2020.103628
Lenahan T., LoCasale-Crouch J., Chamberlain C., Williford A., Downer J., Whittaker J., Miller L. (2022). Examining the association between neighborhood conditions and school readiness across low and highly segregated school attendance boundaries. Frontiers in Education, 7(), -. Frontiers Media S.A..https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2022.932558
Dove-Medows E., Misra D.P., Benkert R., Giurgescu C. (2022). A Qualitative Approach to the Dimensions of Segregation among Pregnant Black Women. Journal of Urban Health, 99(4), 692-700. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11524-022-00661-3
Nenko A., Nedoseka E., Kurilova M. (2022). “NEIGHBORHOODNESS” OF URBAN SERVICES AS A DIMENSION OF SPATIAL SEGREGATION; [«СОСЕДСКОСТЬ» ГОРОДСКИХ СЕРВИСОВ КАК ИЗМЕРЕНИЕ ПРОСТРАНСТВЕННОЙ СЕГРЕГАЦИИ]. Laboratorium: Russian Review of Social Research, 14(3), 34-58. Centre for Independent Social Research.https://doi.org/10.25285/2078-1938-2022-14-3-34-58
Sowgat T., Roy S. (2022). Neighborhood segregation in Dhaka. Journal of Urban Affairs, -. Taylor and Francis Ltd..https://doi.org/10.1080/07352166.2022.2119861
