Racial housing segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===== Date and country of first publication<ref>Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).</ref>===== | |||
1995<br> | 1995<br> | ||
United States | United States | ||
===== Definition ===== | |||
Racial housing segregation refers to the practice of dividing residential areas by race, typically resulting in distinct neighborhoods where people from different racial backgrounds are disproportionately concentrated. This practice has been historically prevalent in many countries, including the United States, where it was reinforced through discriminatory laws and policies such as redlining and restrictive covenants. | Racial housing segregation refers to the practice of dividing residential areas by race, typically resulting in distinct neighborhoods where people from different racial backgrounds are disproportionately concentrated. This practice has been historically prevalent in many countries, including the United States, where it was reinforced through discriminatory laws and policies such as redlining and restrictive covenants. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 13: | ||
Efforts to address racial housing segregation often involve promoting fair housing policies, providing affordable housing options in diverse neighborhoods, and combating discriminatory practices in the real estate market. Encouraging integration and creating opportunities for residents of all backgrounds to live in inclusive neighborhoods is seen as crucial to breaking the cycle of segregation and fostering greater equity and social cohesion. | Efforts to address racial housing segregation often involve promoting fair housing policies, providing affordable housing options in diverse neighborhoods, and combating discriminatory practices in the real estate market. Encouraging integration and creating opportunities for residents of all backgrounds to live in inclusive neighborhoods is seen as crucial to breaking the cycle of segregation and fostering greater equity and social cohesion. | ||
===== Synonyms ===== | |||
The following terms are synonymous with racial housing segregation: | |||
racialized housing segregation. | |||
References and literature addressing this segregation form under these synonymous terms can be found below. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
==Related segregation forms== | |||
Racial housing segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms: | |||
[[racial segregation]], [[residential segregation]], [[housing segregation]] | |||
[[File:racial_housing_segregation.png|780x780px]] | |||
This visualization is based on the study [[Segregation_Wiki:About| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
== | {{NoteAI}} | ||
==Racial housing segregation appears in the following literature== | |||
Farley J.E. ( | Farley J.E. (1995). Race still matters: The Minimal Role of Income and Housing Cost as Causes of Housing Segregation in St. Louis, 1990. ''Urban Affairs Review'', ''31''(2), 244-254. https://doi.org/10.1177/107808749503100207 | ||
Farley J.E. (2005). Race, not class: Explaining racial housing segregation in the St. Louis metropolitan area, 2000. ''Sociological Focus'', ''38''(2), 133-150. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380237.2005.10571261 | |||
Zhang J., Zheng L. (2015). Are people willing to pay for less segregation? Evidence from U.S. internal migration. ''Regional Science and Urban Economics'', ''53''(), 97-112. Elsevier.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2015.05.002 | |||
Seru E. (2021). Critical, Interdisciplinary, And Collaborative Approaches To Virtual Community Engaged Learning During The Covid 19 Pandemic And Social Unrest In The Twin Cities. ''Journal of Higher Education Outreach and Engagement'', ''25''(3), 79-90. University of Georgia.https://doi.org/ | |||
Latest revision as of 07:17, 16 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1][edit | edit source]
1995
United States
Definition[edit | edit source]
Racial housing segregation refers to the practice of dividing residential areas by race, typically resulting in distinct neighborhoods where people from different racial backgrounds are disproportionately concentrated. This practice has been historically prevalent in many countries, including the United States, where it was reinforced through discriminatory laws and policies such as redlining and restrictive covenants.
Racial housing segregation has its roots in institutional racism and racial prejudice, as it emerged as a means to maintain racial hierarchy and control. By separating communities along racial lines, it perpetuates inequalities and disadvantages faced by minority groups, particularly African Americans.
The effects of racial housing segregation are far-reaching and have profound implications for various aspects of life. It contributes to disparities in access to quality education, healthcare, employment opportunities, and other resources. Segregated neighborhoods often lack essential infrastructure and public services, leading to a cycle of poverty and limited social mobility for those residing in these areas.
Although explicit racial discrimination in housing has been banned since the Fair Housing Act of 1968 in the United States, racial housing segregation persists due to continuing socioeconomic disparities and the legacy of past discriminatory practices. Additionally, some argue that less overt forms of housing discrimination such as exclusionary zoning and differential mortgage lending practices contribute to ongoing segregation patterns.
Efforts to address racial housing segregation often involve promoting fair housing policies, providing affordable housing options in diverse neighborhoods, and combating discriminatory practices in the real estate market. Encouraging integration and creating opportunities for residents of all backgrounds to live in inclusive neighborhoods is seen as crucial to breaking the cycle of segregation and fostering greater equity and social cohesion.
Synonyms[edit | edit source]
The following terms are synonymous with racial housing segregation:
racialized housing segregation.
References and literature addressing this segregation form under these synonymous terms can be found below.
See also[edit | edit source]
Related segregation forms[edit | edit source]
Racial housing segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
racial segregation, residential segregation, housing segregation
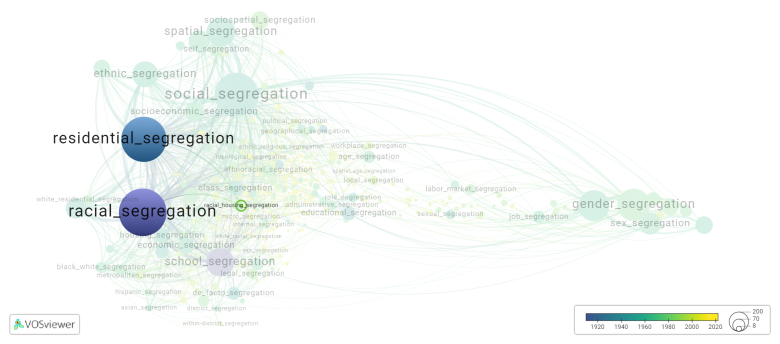
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References[edit | edit source]
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Racial housing segregation appears in the following literature[edit | edit source]
Farley J.E. (1995). Race still matters: The Minimal Role of Income and Housing Cost as Causes of Housing Segregation in St. Louis, 1990. Urban Affairs Review, 31(2), 244-254. https://doi.org/10.1177/107808749503100207
Farley J.E. (2005). Race, not class: Explaining racial housing segregation in the St. Louis metropolitan area, 2000. Sociological Focus, 38(2), 133-150. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380237.2005.10571261
Zhang J., Zheng L. (2015). Are people willing to pay for less segregation? Evidence from U.S. internal migration. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 53(), 97-112. Elsevier.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2015.05.002
Seru E. (2021). Critical, Interdisciplinary, And Collaborative Approaches To Virtual Community Engaged Learning During The Covid 19 Pandemic And Social Unrest In The Twin Cities. Journal of Higher Education Outreach and Engagement, 25(3), 79-90. University of Georgia.https://doi.org/
