Income segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Income segregation refers to the division of communities or neighborhoods based on income levels. This can manifest in various ways, such as gated communities for higher income households, or low-income housing projects that isolate lower-income individuals from the rest of the community. Income segregation can have negative consequences, such as limiting opportunities for social mobility and exacerbating income inequality. It can also lead to social isolation and perpetuate stereotypes and misconceptions about people of different income levels. Efforts to address income segregation may involve policies aimed at promoting mixed-income housing developments, improving access to affordable housing, and increasing economic opportunities for all residents. | Income segregation refers to the division of communities or neighborhoods based on income levels. This can manifest in various ways, such as gated communities for higher income households, or low-income housing projects that isolate lower-income individuals from the rest of the community. Income segregation can have negative consequences, such as limiting opportunities for social mobility and exacerbating income inequality. It can also lead to social isolation and perpetuate stereotypes and misconceptions about people of different income levels. Efforts to address income segregation may involve policies aimed at promoting mixed-income housing developments, improving access to affordable housing, and increasing economic opportunities for all residents. | ||
===== | ===== Synonyms ===== | ||
The following terms are synonymous with income segregation: | |||
individual level segregation | individual level segregation. | ||
References and literature addressing this segregation form under these synonymous terms can be found below. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
==Income | ==Related segregation forms== | ||
Income segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms: | |||
[[residential segregation]], [[social segregation]], [[racial segregation]], [[spatial segregation]], [[socioeconomic segregation]], [[neighborhood segregation]], [[racial residential segregation]], [[school segregation]], [[ethnic segregation]], [[economic segregation]], [[urban segregation]], [[class segregation]], [[neighborhood economic segregation]], [[educational segregation]], [[sociospatial segregation]], [[spatial income segregation]], [[religious segregation]], [[ethnoracial segregation]], [[housing segregation]], [[within-school segregation]], [[homeownership segregation]] | |||
[[File:income_segregation.png|780x780px]] | |||
This visualization is based on the study [[Segregation_Wiki:About| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
{{NoteAI}} | {{NoteAI}} | ||
==Income | ==Income segregation appears in the following literature== | ||
Stahura J.M. (1984 | Stahura J.M. (1984). A research note on the metropolitan determinants of suburban persistence. ''Social Forces'', ''62''(3), 767-774. https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/62.3.767 | ||
Coulibaly M. (1993 | Coulibaly M. (1993). Racial and Income Segregation in Low Income Housing: 1934 1992. ''Review of Radical Political Economics'', ''25''(3), 104-112. https://doi.org/10.1177/048661349302500313 | ||
Massey D.S., Eggers M.L. (1993 | Massey D.S., Eggers M.L. (1993). The spatial concentration of affluence and poverty during the 1970s. ''Urban Affairs Review'', ''29''(2), 299-315. https://doi.org/10.1177/004208169302900206 | ||
Abramson A.J., Tobin M.S., VanderGoot M.R. (1995 | Abramson A.J., Tobin M.S., VanderGoot M.R. (1995). The Changing Geography of Metropolitan Opportunity: The Segregation of the Poor in U.S. Metropolitan Areas, 1970 to 1990. ''Housing Policy Debate'', ''6''(1), 45-72. https://doi.org/10.1080/10511482.1995.9521181 | ||
Van Kempen R., Priemus H. (1999 | Van Kempen R., Priemus H. (1999). Undivided cities in the Netherlands: Present situation and political rhetoric. ''Housing Studies'', ''14''(5), 641-657. Carfax Publishing Company.https://doi.org/10.1080/02673039982650 | ||
Fong E., Shibuya K. ( | Fong E., Shibuya K. (2). The spatial separation of the poor in Canadian cities. ''Demography'', ''37''(4), 449-459. Duke University Press.https://doi.org/10.2307/2648071 | ||
Ross N.A., Nobrega K., Dunn J. (2001 | Ross N.A., Nobrega K., Dunn J. (2001). Income segregation, income inequality and mortality in North American metropolitan areas. ''GeoJournal'', ''53''(2), 117-124. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015720518936 | ||
Nechyba T. (2003 | Nechyba T. (2003). School finance, spatial income segregation, and the nature of communities. ''Journal of Urban Economics'', ''54''(1), 61-88. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1016/S0094-1190(03)00041-X | ||
Pendall R., Carruthers J.I. (2003 | Pendall R., Carruthers J.I. (2003). Does density exacerbate income segregation? Evidence from U.S. Metropolitan Areas, 1980 to 2000. ''Housing Policy Debate'', ''14''(4), 541-589. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/10511482.2003.9521487 | ||
Fischer M.J. (2003 | Fischer M.J. (2003). The relative importance of income and race in determining residential outcomes in U.S. urban areas, 1970 2000. ''Urban Affairs Review'', ''38''(5), 669-696. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078087403038005003 | ||
Ross N.A., Houle C., Dunn J.R., Aye M. (2004 | Ross N.A., Houle C., Dunn J.R., Aye M. (2004). Dimensions and dynamics of residential segregation by income in urban Canada, 1991 1996. ''Canadian Geographer'', ''48''(4), 433-445. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0008-3658.2004.00069.x | ||
Pendall R. (2005 | Pendall R. (2005). Does density exacerbate income segregation? Evidence from U.S. Metropolitan areas, 1980 1990. ''Desegregating The City: Ghettos, Enclaves, and Inequality'', 175-199. State University of New York Press.https://doi.org/ | ||
Burgess S., Wilson D. (2005 | Burgess S., Wilson D. (2005). Ethnic segregation in England's schools. ''Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers'', ''30''(1), 20-36. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-5661.2005.00149.x | ||
Varady D.P. (2005 | Varady D.P. (2005). Desegregating the city: Ghettos, enclaves, and inequality. ''Desegregating the City: Ghettos, Enclaves, and Inequality'', 1-310. State University of New York Press.https://doi.org/ | ||
Schmidheiny K. (2006 | Schmidheiny K. (2006). Income segregation from local income taxation when households differ in both preferences and incomes. ''Regional Science and Urban Economics'', ''36''(2), 270-299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2005.10.003 | ||
Schmidheiny K. (2006 | Schmidheiny K. (2006). Income segregation and local progressive taxation: Empirical evidence from Switzerland. ''Journal of Public Economics'', ''90''(3), 429-458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2005.09.003 | ||
Schmidheiny K. (2006 | Schmidheiny K. (2006). Income segregation and local progressive taxation: Empirical evidence from Switzerland. ''Journal of Public Economics'', ''90''(3), 429-458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2005.09.003 | ||
Hodler R., Schmidheiny K. (2006 | Hodler R., Schmidheiny K. (2006). How fiscal decentralization flattens progressive taxes. ''FinanzArchiv'', ''62''(2), 281-304. https://doi.org/10.1628/001522106X120695 | ||
Reardon S.F., Yun J.T., Kurlaender M. (2006 | Reardon S.F., Yun J.T., Kurlaender M. (2006). Implications of income based school assignment policies for racial school segregation. ''Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis'', ''28''(1), 49-75. https://doi.org/10.3102/01623737028001049 | ||
Dawkins C.J. (2007 | Dawkins C.J. (2007). Space and the measurement of income segregation. ''Journal of Regional Science'', ''47''(2), 255-272. Blackwell Publishing Inc..https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9787.2007.00508.x | ||
Galbraith J.K., Hale J.T. (2008 | Galbraith J.K., Hale J.T. (2008). State income inequality and presidential election turnout and outcomes. ''Social Science Quarterly'', ''89''(4), 887-901. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6237.2008.00589.x | ||
Oreopoulos P. (2008 | Oreopoulos P. (2008). Neighbourhood effects in Canada: A critique. ''Canadian Public Policy'', ''34''(2), 237-258. https://doi.org/10.3138/cpp.34.2.237 | ||
Wood G., Berry M., Taylor E., Nygaard C. (2008 | Wood G., Berry M., Taylor E., Nygaard C. (2008). Community mix, affordable housing and metropolitan planning strategy in Melbourne. ''Built Environment'', ''34''(3), 273-290. https://doi.org/10.2148/benv.34.3.273 | ||
Downes T. (2009 | Downes T. (2009). School Finance Reform. ''International Encyclopedia of Education, Third Edition'', 216-221. Elsevier.https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-044894-7.01242-2 | ||
Watson T. (2009 | Watson T. (2009). Inequality and the measurement of residential segregation by income in american neighborhoods. ''Review of Income and Wealth'', ''55''(3), 820-844. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-4991.2009.00346.x | ||
Watson T. (2009 | Watson T. (2009). Inequality and the measurement of residential segregation by income in american neighborhoods. ''Review of Income and Wealth'', ''55''(3), 820-844. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-4991.2009.00346.x | ||
Dawkins C.J. (2009 | Dawkins C.J. (2009). Exploring changes in the spatial pattern of income segregation during the 1990s. ''Research on Economic Inequality'', ''17''(), 159-170. https://doi.org/10.1108/S1049-2585(2009)0000017012 | ||
Freeman L. (2009 | Freeman L. (2009). Neighbourhood diversity, metropolitan segregation and gentrification: What are the links in the US?. ''Urban Studies'', ''46''(10), 2079-2101. https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098009339426 | ||
Rothwell J.T., Massey D.S. ( | Rothwell J.T., Massey D.S. (201). Density zoning and class segregation in U.S. metropolitan areas. ''Social Science Quarterly'', ''91''(5), 1123-1143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6237.2010.00724.x | ||
Wu J. ( | Wu J. (201). Economic fundamentals and urban suburban disparities. ''Journal of Regional Science'', ''50''(2), 570-591. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9787.2010.00665.x | ||
Schaltegger C.A., Somogyi F., Sturm J.-E. (2011 | Schaltegger C.A., Somogyi F., Sturm J.-E. (2011). Tax competition and income sorting: Evidence from the Zurich metropolitan area. ''European Journal of Political Economy'', ''27''(3), 455-470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpoleco.2011.01.004 | ||
Finney M.M., Goetzke F., Yoon M.J. (2011 | Finney M.M., Goetzke F., Yoon M.J. (2011). Income sorting and the demand for clean air: Evidence from southern California. ''Land Economics'', ''87''(1), 19-27. University of Wisconsin Press.https://doi.org/10.3368/le.87.1.19 | ||
Rey S.J., Folch D.C. (2011 | Rey S.J., Folch D.C. (2011). Impact of spatial effects on income segregation indices. ''Computers, Environment and Urban Systems'', ''35''(6), 431-441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2011.07.008 | ||
Reardon S.F., Bischoff K. (2011 | Reardon S.F., Bischoff K. (2011). Income inequality and income segregation. ''American Journal of Sociology'', ''116''(4), 1092-1153. https://doi.org/10.1086/657114 | ||
Bayer P., McMillan R. (2012 | Bayer P., McMillan R. (2012). Tiebout sorting and neighborhood stratification. ''Journal of Public Economics'', ''96''(11-12), 1129-1143. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2012.02.006 | ||
Quillian L. (2012 | Quillian L. (2012). Segregation and Poverty Concentration: The Role of Three Segregations. ''American Sociological Review'', ''77''(3), 354-379. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003122412447793 | ||
Gauvin L., Vignes A., Nadal J.-P. (2013 | Gauvin L., Vignes A., Nadal J.-P. (2013). Modeling urban housing market dynamics: Can the socio spatial segregation preserve some social diversity?. ''Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control'', ''37''(7), 1300-1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jedc.2013.03.001 | ||
Gauvin L., Vignes A., Nadal J.-P. (2013 | Gauvin L., Vignes A., Nadal J.-P. (2013). Modeling urban housing market dynamics: Can the socio spatial segregation preserve some social diversity?. ''Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control'', ''37''(7), 1300-1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jedc.2013.03.001 | ||
Meltzer R. (2013 | Meltzer R. (2013). Do Homeowners Associations Affect Citywide Segregation? Evidence From Florida Municipalities. ''Housing Policy Debate'', ''23''(4), 688-713. https://doi.org/10.1080/10511482.2013.812571 | ||
Enström Öst C., Söderberg B., Wilhelmsson M. (2014 | Enström Öst C., Söderberg B., Wilhelmsson M. (2014). Household allocation and spatial distribution in a market under ("soft") rent control. ''Journal of Policy Modeling'', ''36''(2), 353-372. Elsevier.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpolmod.2014.01.002 | ||
Walks A. (2014 | Walks A. (2014). From Financialization to Sociospatial Polarization of the City? Evidence from Canada. ''Economic Geography'', ''90''(1), 33-66. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecge.12024 | ||
De Fraja G., Martínez-Mora F. (2014 | De Fraja G., Martínez-Mora F. (2014). The desegregating effect of school tracking. ''Journal of Urban Economics'', ''80''(), 164-177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jue.2014.01.001 | ||
De Fraja G., Martínez-Mora F. (2014 | De Fraja G., Martínez-Mora F. (2014). The desegregating effect of school tracking. ''Journal of Urban Economics'', ''80''(), 164-177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jue.2014.01.001 | ||
Modai-Snir T., Plaut P.O. (2015 | Modai-Snir T., Plaut P.O. (2015). Intra metropolitan residential mobility and income sorting trends. ''Letters in Spatial and Resource Sciences'', ''8''(3), 291-305. Springer Verlag.https://doi.org/10.1007/s12076-014-0133-z | ||
Musterd S., Van Gent W. (2015 | Musterd S., Van Gent W. (2015). Changing welfare context and income segregation in Amsterdam and its metropolitan area. ''Socio-Economic Segregation in European Capital Cities: East Meets West'', 55-79. Taylor and Francis Inc..https://doi.org/ | ||
Owens A. (2015 | Owens A. (2015). Assisted Housing and Income Segregation among Neighborhoods in U.S. Metropolitan Areas. ''Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science'', ''660''(1), 98-116. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0002716215576106 | ||
Yang Y., Auchincloss A.H., Rodriguez D.A., Brown D.G., Riolo R., Diez-Roux A.V. (2015 | Yang Y., Auchincloss A.H., Rodriguez D.A., Brown D.G., Riolo R., Diez-Roux A.V. (2015). Modeling spatial segregation and travel cost influences on utilitarian walking: Towards policy intervention. ''Computers, Environment and Urban Systems'', ''51''(), 59-69. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2015.01.007 | ||
Owens A., Reardon S.F., Jencks C. (2016 | Owens A., Reardon S.F., Jencks C. (2016). Income Segregation Between Schools and School Districts. ''American Educational Research Journal'', ''53''(4), 1159-1197. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831216652722 | ||
Williamson P. (2016 | Williamson P. (2016). Small Area Incomes: Their Spatial Variability and the Relative Efficacy of Proxy, Geodemographic, Imputed and Model Based Estimates. ''Applied Spatial Analysis and Policy'', ''9''(4), 463-489. Springer Netherlands.https://doi.org/10.1007/s12061-015-9163-1 | ||
Andersson R., Hedman L. (2016 | Andersson R., Hedman L. (2016). Economic decline and residential segregation: a Swedish study with focus on Malmö. ''Urban Geography'', ''37''(5), 748-768. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/02723638.2015.1133993 | ||
Owens A. (2016 | Owens A. (2016). Inequality in Children’s Contexts: Income Segregation of Households with and without Children. ''American Sociological Review'', ''81''(3), 549-574. American Sociological Association.https://doi.org/10.1177/0003122416642430 | ||
Quillian L., Lagrange H. (2016 | Quillian L., Lagrange H. (2016). Socioeconomic Segregation in Large Cities in France and the United States. ''Demography'', ''53''(4), 1051-1084. Springer Science and Business Media, LLC.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-016-0491-9 | ||
Agostini C.A., Hojman D., Román A., Valenzuela L. (2016 | Agostini C.A., Hojman D., Román A., Valenzuela L. (2016). Income residential segregation in Greater Santiago, 1992 2002: A robust estimation; [Segregación residencial de ingresos en el Gran Santiago, 1992 2002: Una estimación robusta]. ''Eure'', ''42''(127), 159-184. Revista de Geografia Norte Grande.https://doi.org/10.4067/S0250-71612016000300007 | ||
Ruiz-Rivera N., Suárez M., Delgado-Campos J. (2016 | Ruiz-Rivera N., Suárez M., Delgado-Campos J. (2016). Urban segregation and local retail environments. Evidence from Mexico City. ''Habitat International'', ''54''(), 58-64. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2014.09.001 | ||
Wilson W.J. (2016 | Wilson W.J. (2016). Black youths, joblessness, and the other side of ‘Black Lives Matter’. ''Ethnic and Racial Studies'', ''39''(8), 1450-1457. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/01419870.2016.1153689 | ||
Lens M.C., Monkkonen P. (2016 | Lens M.C., Monkkonen P. (2016). Do Strict Land Use Regulations Make Metropolitan Areas More Segregated by Income?. ''Journal of the American Planning Association'', ''82''(1), 6-21. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/01944363.2015.1111163 | ||
Lens M.C., Monkkonen P. (2016 | Lens M.C., Monkkonen P. (2016). Do Strict Land Use Regulations Make Metropolitan Areas More Segregated by Income?. ''Journal of the American Planning Association'', ''82''(1), 6-21. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/01944363.2015.1111163 | ||
Johnson O.C.A. (2016 | Johnson O.C.A. (2016). Inclusion, exclusion, and the “new” economic inequality. ''Texas Law Review'', ''94''(7), 1647-1665. School of Law Publications.https://doi.org/ | ||
Saporito S. (2017 | Saporito S. (2017). Shaping Income Segregation in Schools: The Role of School Attendance Zone Geography. ''American Educational Research Journal'', ''54''(6), 1345-1377. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831217724116 | ||
Saporito S. (2017 | Saporito S. (2017). Shaping Income Segregation in Schools: The Role of School Attendance Zone Geography. ''American Educational Research Journal'', ''54''(6), 1345-1377. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831217724116 | ||
Wolfson M., Gribble S., Beall R. (2017 | Wolfson M., Gribble S., Beall R. (2017). Exploring Contingent Inequalities: Building the Theoretical Health Inequality Model. ''Springer Series on Demographic Methods and Population Analysis'', ''41''(), 487-513. Springer Science and Business Media B.V..https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32283-4_17 | ||
Iceland J., Hernandez E. (2017 | Iceland J., Hernandez E. (2017). Understanding trends in concentrated poverty: 1980 2014. ''Social Science Research'', ''62''(), 75-95. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssresearch.2016.09.001 | ||
Larson S.J. (2018 | Larson S.J. (2018). Examining the Efficacy of Title VI Social Equity Analysis: A Comparative Case Study of Transit Access and Neighborhood Segregation Outcomes Over Time. ''Public Integrity'', ''20''(4), 344-357. Taylor and Francis Ltd..https://doi.org/10.1080/10999922.2018.1441595 | ||
Garcia-López M.-À., Moreno-Monroy A.I. (2018 | Garcia-López M.-À., Moreno-Monroy A.I. (2018). Income segregation in monocentric and polycentric cities: Does urban form really matter?. ''Regional Science and Urban Economics'', ''71''(), 62-79. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2018.05.003 | ||
Heilmann K. (2018 | Heilmann K. (2018). Transit access and neighborhood segregation. Evidence from the Dallas light rail system. ''Regional Science and Urban Economics'', ''73''(), 237-250. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2018.10.007 | ||
Bond T.N., Salisbury L. (2018 | Bond T.N., Salisbury L. (2018). Local Information, Income Segregation, and Geographic Mobility. ''B.E. Journal of Economic Analysis and Policy'', ''18''(3), -. De Gruyter.https://doi.org/10.1515/bejeap-2017-0314 | ||
Reardon S.F., Bischoff K., Owens A., Townsend J.B. (2018 | Reardon S.F., Bischoff K., Owens A., Townsend J.B. (2018). Has Income Segregation Really Increased? Bias and Bias Correction in Sample Based Segregation Estimates. ''Demography'', ''55''(6), 2129-2160. Springer Science and Business Media, LLC.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-018-0721-4 | ||
Bélec J., Harris R., Rose G. (2018 | Bélec J., Harris R., Rose G. (2018). The Federal Impact on Early Postwar Suburbanization. ''Housing Policy Debate'', ''28''(6), 854-875. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/10511482.2018.1474124 | ||
Logan J.R., Foster A., Ke J., Li F. (2018 | Logan J.R., Foster A., Ke J., Li F. (2018). The uptick in income segregation: Real trend or random sampling variation?. ''American Journal of Sociology'', ''124''(1), 185-222. University of Chicago Press.https://doi.org/10.1086/697528 | ||
Reardon S.F., Bischoff K. (2018 | Reardon S.F., Bischoff K. (2018). Income Inequality and Income Segregation. ''Social Stratification: Class, Race, and Gender in Sociological Perspective'', 1023-1034. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429494642-123 | ||
Owens A. (2018 | Owens A. (2018). Income Segregation between School Districts and Inequality in Students’ Achievement. ''Sociology of Education'', ''91''(1), 1-27. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0038040717741180 | ||
Reardon S.F., Bischoff K. (2018 | Reardon S.F., Bischoff K. (2018). Income Inequality and Income Segregation. ''Inequality in the 21st Century: A Reader'', 426-435. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429499821-73 | ||
Reardon S.F., Bischoff K. (2018 | Reardon S.F., Bischoff K. (2018). Income Inequality and Income Segregation. ''Inequality in the 21st Century: A Reader'', 426-435. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429499821-73 | ||
Li M., Johnson S.B., Newman S., Riley A.W. (2019 | Li M., Johnson S.B., Newman S., Riley A.W. (2019). Residential mobility and long term exposure to neighborhood poverty among children born in poor families: A U.S. longitudinal cohort study. ''Social Science and Medicine'', ''226''(), 69-76. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2019.02.042 | ||
Pangallo M., Nadal J.-P., Vignes A. (2019 | Pangallo M., Nadal J.-P., Vignes A. (2019). Residential income segregation: A behavioral model of the housing market. ''Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization'', ''159''(), 15-35. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2019.01.010 | ||
Pangallo M., Nadal J.-P., Vignes A. (2019 | Pangallo M., Nadal J.-P., Vignes A. (2019). Residential income segregation: A behavioral model of the housing market. ''Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization'', ''159''(), 15-35. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2019.01.010 | ||
Taylor K., Anderson J., Frankenberg E. (2019 | Taylor K., Anderson J., Frankenberg E. (2019). School and Residential Segregation in School Districts with Voluntary Integration Policies. ''Peabody Journal of Education'', ''94''(4), 371-387. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/0161956X.2019.1648950 | ||
Bischoff K., Owens A. (2019 | Bischoff K., Owens A. (2019). The Segregation of Opportunity: Social and Financial Resources in the Educational Contexts of Lower and Higher Income Children, 1990 2014. ''Demography'', ''56''(5), 1635-1664. Springer Science and Business Media, LLC.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-019-00817-y | ||
Galster G., Turner L.M. (2019 | Galster G., Turner L.M. (2019). Status Aversion, Attraction and Discrepancy as Drivers of Neighborhood Selection. ''City and Community'', ''18''(3), 937-964. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/cico.12435 | ||
Galster G., Turner L.M. (2019 | Galster G., Turner L.M. (2019). Status Aversion, Attraction and Discrepancy as Drivers of Neighborhood Selection. ''City and Community'', ''18''(3), 937-964. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/cico.12435 | ||
Pearman F.A., II (2019 | Pearman F.A., II (2019). The Effect of Neighborhood Poverty on Math Achievement: Evidence From a Value Added Design. ''Education and Urban Society'', ''51''(2), 289-307. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0013124517715066 | ||
Christafore D., Leguizamon S. (2019 | Christafore D., Leguizamon S. (2019). Neighbourhood inequality spillover effects of gentrification. ''Papers in Regional Science'', ''98''(3), 1469-1484. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/pirs.12405 | ||
Guo C., Buchmann C.M., Schwarz N. (2019 | Guo C., Buchmann C.M., Schwarz N. (2019). Linking urban sprawl and income segregation Findings from a stylized agent based model. ''Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science'', ''46''(3), 469-489. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/2399808317719072 | ||
Owens A. (2019 | Owens A. (2019). Building Inequality: Housing Segregation and Income Segregation. ''Sociological Science'', ''6''(), -. Society for Sociological Science.https://doi.org/10.15195/v6.a19 | ||
Yavaş M. (2019 | Yavaş M. (2019). Dissecting income segregation: Impacts of concentrated affluence on segregation of poverty. ''Journal of Mathematical Sociology'', ''43''(1), 1-22. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/0022250X.2018.1476858 | ||
Sampson R.J. (2019 | Sampson R.J. (2019). Neighbourhood effects and beyond: Explaining the paradoxes of inequality in the changing American metropolis. ''Urban Studies'', ''56''(1), 3-32. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098018795363 | ||
Neuman S.B., Moland N. (2019 | Neuman S.B., Moland N. (2019). Book Deserts: The Consequences of Income Segregation on Children’s Access to Print. ''Urban Education'', ''54''(1), 126-147. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0042085916654525 | ||
Wichowsky A. (2019 | Wichowsky A. (2019). Civic Life in the Divided Metropolis: Social Capital, Collective Action, and Residential Income Segregation. ''Urban Affairs Review'', ''55''(1), 257-287. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/1078087416688097 | ||
Lasso de la Vega C., Volij O. ( | Lasso de la Vega C., Volij O. (202). THE MEASUREMENT OF INCOME SEGREGATION. ''International Economic Review'', ''61''(4), 1479-1500. Blackwell Publishing Inc..https://doi.org/10.1111/iere.12466 | ||
Chetty R., Friedman J.N., Saez E., Turner N., Yagan D. ( | Chetty R., Friedman J.N., Saez E., Turner N., Yagan D. (202). Income Segregation and Intergenerational Mobility across Colleges in the United States. ''Quarterly Journal of Economics'', ''135''(3), 1567-1633. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/qje/qjaa005 | ||
Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. ( | Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. (202). On the link between rail transit and spatial income segregation. ''Applied Geography'', ''125''(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102364 | ||
Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. ( | Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. (202). On the link between rail transit and spatial income segregation. ''Applied Geography'', ''125''(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102364 | ||
Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. ( | Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. (202). On the link between rail transit and spatial income segregation. ''Applied Geography'', ''125''(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102364 | ||
Estep K., Greenberg P. ( | Estep K., Greenberg P. (202). Opting Out: Individualism and Vaccine Refusal in Pockets of Socioeconomic Homogeneity. ''American Sociological Review'', ''85''(6), 957-991. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0003122420960691 | ||
Logan J.R., Foster A., Xu H., Zhang W. ( | Logan J.R., Foster A., Xu H., Zhang W. (202). Income Segregation: Up or Down, and for Whom?. ''Demography'', ''57''(5), 1951-1974. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-020-00917-0 | ||
Logan J.R., Foster A., Xu H., Zhang W. ( | Logan J.R., Foster A., Xu H., Zhang W. (202). Income Segregation: Up or Down, and for Whom?. ''Demography'', ''57''(5), 1951-1974. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-020-00917-0 | ||
Yabe T., Ukkusuri S.V. ( | Yabe T., Ukkusuri S.V. (202). Effects of income inequality on evacuation, reentry and segregation after disasters. ''Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment'', ''82''(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2020.102260 | ||
Ziller C., Spörlein C. ( | Ziller C., Spörlein C. (202). Residential Segregation and Social Trust of Immigrants and Natives: Evidence From the Netherlands. ''Frontiers in Sociology'', ''5''(), -. Frontiers Media S.A..https://doi.org/10.3389/fsoc.2020.00045 | ||
Haddad M.A. ( | Haddad M.A. (202). Residential income segregation and commuting in a Latin American city. ''Applied Geography'', ''117''(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102186 | ||
Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. ( | Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. (202). Impact of new rail transit stations on neighborhood destination choices and income segregation. ''Cities'', ''102''(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2020.102737 | ||
Sampson R.J., Levy B.L. ( | Sampson R.J., Levy B.L. (202). Beyond Residential Segregation: Mobility Based Connectedness and Rates of Violence in Large Cities. ''Race and Social Problems'', ''12''(1), 77-86. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s12552-019-09273-0 | ||
Owens A. ( | Owens A. (202). Unequal Opportunity: School and Neighborhood Segregation in the USA. ''Race and Social Problems'', ''12''(1), 29-41. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s12552-019-09274-z | ||
Drouhot L.G. ( | Drouhot L.G. (202). Income Segregation and the Incomplete Integration of Islam in the Paris Metropolitan Area. ''Socius'', ''6''(), -. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/2378023119899585 | ||
Richards M.P., Stroub K.J. ( | Richards M.P., Stroub K.J. (202). Metropolitan public school district segregation by race and income, 2000 2011. ''Teachers College Record'', ''122''(5), 21-41. Teachers College, Columbia University.https://doi.org/ | ||
Havewala F. (2021 | Havewala F. (2021). The dynamics between the food environment and residential segregation: An analysis of metropolitan areas. ''Food Policy'', ''103''(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2020.102015 | ||
Gallagher R.M. (2021 | Gallagher R.M. (2021). Income segregation's impact on local public expenditures: Evidence from municipalities and school districts, 1980 2010. ''Regional Science and Urban Economics'', ''90''(), -. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2021.103710 | ||
Gallagher R.M. (2021 | Gallagher R.M. (2021). Income segregation's impact on local public expenditures: Evidence from municipalities and school districts, 1980 2010. ''Regional Science and Urban Economics'', ''90''(), -. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2021.103710 | ||
Gallagher R.M. (2021 | Gallagher R.M. (2021). Income segregation's impact on local public expenditures: Evidence from municipalities and school districts, 1980 2010. ''Regional Science and Urban Economics'', ''90''(), -. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2021.103710 | ||
Delmelle E., Nilsson I., Adu P. (2021 | Delmelle E., Nilsson I., Adu P. (2021). Poverty suburbanization, job accessibility, and employment outcomes. ''Social Inclusion'', ''9''(2), 166-178. Cogitatio Press.https://doi.org/10.17645/si.v9i2.3735 | ||
Park H. (2021 | Park H. (2021). Income sorting by specialized services: Service differentiation by overlapping governments. ''Social Science Quarterly'', ''102''(6), 2761-2775. John Wiley and Sons Inc.https://doi.org/10.1111/ssqu.13078 | ||
Taylor K., Frankenberg E. (2021 | Taylor K., Frankenberg E. (2021). Student Assignment Policies and Racial and Income Segregation of Schools, School Attendance Zones, and Neighborhoods. ''Educational Administration Quarterly'', ''57''(5), 747-775. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0013161X211024720 | ||
Zhang T., Duan X., Wong D.W.S., Lu Y. (2021 | Zhang T., Duan X., Wong D.W.S., Lu Y. (2021). Discovering income economic segregation patterns: A residential mobility embedding approach. ''Computers, Environment and Urban Systems'', ''90''(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2021.101709 | ||
Mehta A. (2021 | Mehta A. (2021). SALT, Subsidies, and Subnational Spending. ''Columbia Journal of Law and Social Problems'', ''54''(2), 219-260. Columbia Law Review Association.https://doi.org/ | ||
Modai-Snir T. (2021 | Modai-Snir T. (2021). Increasing Inequality and the Changing Spatial Distribution of Income in Tel Aviv. ''Urban Book Series'', 191-207. Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64569-4_10 | ||
Veneri P., Comandon A., Garcia-López M.-À., Daams M.N. (2021 | Veneri P., Comandon A., Garcia-López M.-À., Daams M.N. (2021). What do divided cities have in common? An international comparison of income segregation. ''Journal of Regional Science'', ''61''(1), 162-188. Blackwell Publishing Inc..https://doi.org/10.1111/jors.12506 | ||
Ismail M., Warsame A., Wilhelmsson M. (2021 | Ismail M., Warsame A., Wilhelmsson M. (2021). Do segregated housing markets have a spillover effect on housing prices in nearby residential areas?. ''Journal of European Real Estate Research'', ''14''(2), 169-186. Emerald Group Holdings Ltd..https://doi.org/10.1108/JERER-06-2020-0037 | ||
Santos M.I.D., Santos G.F.D., Freitas A., Sousa Filho J.F.D., Castro C., Paiva A.S.S., Friche A.A.D.L., Barber S., Caiaffa W.T., Barreto M.L. (2021 | Santos M.I.D., Santos G.F.D., Freitas A., Sousa Filho J.F.D., Castro C., Paiva A.S.S., Friche A.A.D.L., Barber S., Caiaffa W.T., Barreto M.L. (2021). Urban income segregation and homicides: An analysis using Brazilian cities selected by the Salurbal project. ''SSM - Population Health'', ''14''(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssmph.2021.100819 | ||
Santos M.I.D., Santos G.F.D., Freitas A., Sousa Filho J.F.D., Castro C., Paiva A.S.S., Friche A.A.D.L., Barber S., Caiaffa W.T., Barreto M.L. (2021 | Santos M.I.D., Santos G.F.D., Freitas A., Sousa Filho J.F.D., Castro C., Paiva A.S.S., Friche A.A.D.L., Barber S., Caiaffa W.T., Barreto M.L. (2021). Urban income segregation and homicides: An analysis using Brazilian cities selected by the Salurbal project. ''SSM - Population Health'', ''14''(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssmph.2021.100819 | ||
Kulkarni N., Malmendier U. (2022 | Kulkarni N., Malmendier U. (2022). Homeownership segregation. ''Journal of Monetary Economics'', ''129''(), 123-149. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmoneco.2022.05.001 | ||
Wessel T. (2022 | Wessel T. (2022). Business Services, Income Inequality, and Income Segregation in Metropolitan Areas: Direct and Indirect Links. ''Economic Geography'', ''98''(5), 464-486. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/00130095.2022.2074831 | ||
Peters S.J., Carter J.S., III (2022 | Peters S.J., Carter J.S., III (2022). Predictors of Access to Gifted Education: What Makes for a Successful School?. ''Exceptional Children'', ''88''(4), 341-358. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/00144029221081092 | ||
Kim Y., Colabianchi N. (2022 | Kim Y., Colabianchi N. (2022). The Longitudinal Effect of Area Socioeconomic Changes on Obesity: a Longitudinal Cohort Study in the USA from 2003 to 2017. ''Journal of Urban Health'', ''99''(6), 1068-1079. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11524-022-00681-z | ||
Ekenga C.C., Tian R. (2022 | Ekenga C.C., Tian R. (2022). Promoting Food Equity in the Context of Residential Segregation. ''Environmental Justice'', ''15''(6), 346-351. Mary Ann Liebert Inc..https://doi.org/10.1089/env.2021.0029 | ||
Schachner J.N. (2022 | Schachner J.N. (2022). Neighborhood Economic Change in an Era of Metropolitan Divergence. ''Urban Affairs Review'', ''58''(4), 923-959. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/10780874211016940 | ||
Schachner J.N. (2022 | Schachner J.N. (2022). Neighborhood Economic Change in an Era of Metropolitan Divergence. ''Urban Affairs Review'', ''58''(4), 923-959. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/10780874211016940 | ||
Ng M.K.M., Roper J., Lee C.L., Pettit C. (2022 | Ng M.K.M., Roper J., Lee C.L., Pettit C. (2022). The Reflection of Income Segregation and Accessibility Cleavages in Sydney’s House Prices. ''ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information'', ''11''(7), -. MDPI.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11070413 | ||
Ng M.K.M., Roper J., Lee C.L., Pettit C. (2022 | Ng M.K.M., Roper J., Lee C.L., Pettit C. (2022). The Reflection of Income Segregation and Accessibility Cleavages in Sydney’s House Prices. ''ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information'', ''11''(7), -. MDPI.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11070413 | ||
Dalane K., Marcotte D.E. (2022 | Dalane K., Marcotte D.E. (2022). The Segregation of Students by Income in Public Schools. ''Educational Researcher'', ''51''(4), 245-254. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X221081853 | ||
Beaubrun-Diant K., Maury T.-P. (2022 | Beaubrun-Diant K., Maury T.-P. (2022). On the Impact of Public Housing on Income Segregation in France. ''Demography'', ''59''(2), 685-706. Duke University Press.https://doi.org/10.1215/00703370-9807596 | ||
Quick M., Revington N. (2022 | Quick M., Revington N. (2022). Exploring the global and local patterns of income segregation in Toronto, Canada: A multilevel multigroup modeling approach. ''Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science'', ''49''(2), 637-653. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/23998083211021419 | ||
Quick M., Revington N. (2022 | Quick M., Revington N. (2022). Exploring the global and local patterns of income segregation in Toronto, Canada: A multilevel multigroup modeling approach. ''Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science'', ''49''(2), 637-653. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/23998083211021419 | ||
Won J. (2022 | Won J. (2022). Exploring Spatial Clustering Over Time and Spillover Effects of the Low Income Housing Tax Credit on Neighborhood Level Income Segregation. ''Urban Affairs Review'', ''58''(3), 799-831. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/1078087420973436 | ||
Kim H., Schmidt N.M., Osypuk T.L., Thyden N., Rehkopf D. (2022 | Kim H., Schmidt N.M., Osypuk T.L., Thyden N., Rehkopf D. (2022). Effects of housing vouchers on the long term exposure to neighbourhood opportunity among low income families: the moving to opportunity experiment. ''Housing Studies'', ''38''(1), 128-151. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/02673037.2022.2112154 | ||
Adu P., Delmelle E.C. (2022 | Adu P., Delmelle E.C. (2022). Spatial Variations in Exclusionary Criteria from Online Rental Advertisements. ''Professional Geographer'', ''74''(4), 704-714. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/00330124.2022.2061537 | ||
South S.J., Huang Y., Spring A. (2022 | South S.J., Huang Y., Spring A. (2022). Proximate sources of growth in neighborhood income segregation: Class selective migration versus in situ change. ''Social Science Research'', ''101''(), -. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssresearch.2021.102624 | ||
Latest revision as of 07:17, 16 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1][edit | edit source]
1984
United States
Definition[edit | edit source]
Income segregation refers to the division of communities or neighborhoods based on income levels. This can manifest in various ways, such as gated communities for higher income households, or low-income housing projects that isolate lower-income individuals from the rest of the community. Income segregation can have negative consequences, such as limiting opportunities for social mobility and exacerbating income inequality. It can also lead to social isolation and perpetuate stereotypes and misconceptions about people of different income levels. Efforts to address income segregation may involve policies aimed at promoting mixed-income housing developments, improving access to affordable housing, and increasing economic opportunities for all residents.
Synonyms[edit | edit source]
The following terms are synonymous with income segregation:
individual level segregation.
References and literature addressing this segregation form under these synonymous terms can be found below.
See also[edit | edit source]
Related segregation forms[edit | edit source]
Income segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
residential segregation, social segregation, racial segregation, spatial segregation, socioeconomic segregation, neighborhood segregation, racial residential segregation, school segregation, ethnic segregation, economic segregation, urban segregation, class segregation, neighborhood economic segregation, educational segregation, sociospatial segregation, spatial income segregation, religious segregation, ethnoracial segregation, housing segregation, within-school segregation, homeownership segregation
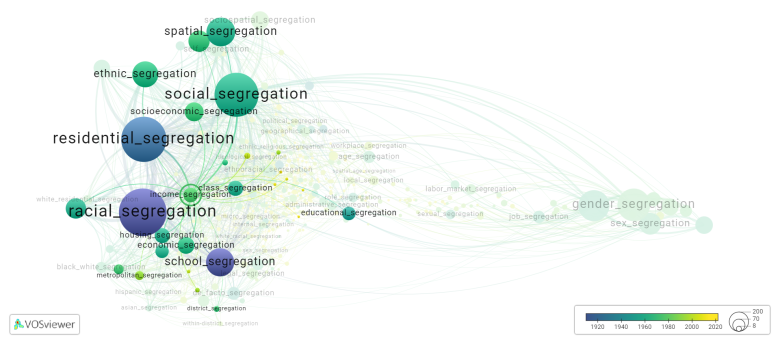
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References[edit | edit source]
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Income segregation appears in the following literature[edit | edit source]
Stahura J.M. (1984). A research note on the metropolitan determinants of suburban persistence. Social Forces, 62(3), 767-774. https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/62.3.767
Coulibaly M. (1993). Racial and Income Segregation in Low Income Housing: 1934 1992. Review of Radical Political Economics, 25(3), 104-112. https://doi.org/10.1177/048661349302500313
Massey D.S., Eggers M.L. (1993). The spatial concentration of affluence and poverty during the 1970s. Urban Affairs Review, 29(2), 299-315. https://doi.org/10.1177/004208169302900206
Abramson A.J., Tobin M.S., VanderGoot M.R. (1995). The Changing Geography of Metropolitan Opportunity: The Segregation of the Poor in U.S. Metropolitan Areas, 1970 to 1990. Housing Policy Debate, 6(1), 45-72. https://doi.org/10.1080/10511482.1995.9521181
Van Kempen R., Priemus H. (1999). Undivided cities in the Netherlands: Present situation and political rhetoric. Housing Studies, 14(5), 641-657. Carfax Publishing Company.https://doi.org/10.1080/02673039982650
Fong E., Shibuya K. (2). The spatial separation of the poor in Canadian cities. Demography, 37(4), 449-459. Duke University Press.https://doi.org/10.2307/2648071
Ross N.A., Nobrega K., Dunn J. (2001). Income segregation, income inequality and mortality in North American metropolitan areas. GeoJournal, 53(2), 117-124. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015720518936
Nechyba T. (2003). School finance, spatial income segregation, and the nature of communities. Journal of Urban Economics, 54(1), 61-88. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1016/S0094-1190(03)00041-X
Pendall R., Carruthers J.I. (2003). Does density exacerbate income segregation? Evidence from U.S. Metropolitan Areas, 1980 to 2000. Housing Policy Debate, 14(4), 541-589. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/10511482.2003.9521487
Fischer M.J. (2003). The relative importance of income and race in determining residential outcomes in U.S. urban areas, 1970 2000. Urban Affairs Review, 38(5), 669-696. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078087403038005003
Ross N.A., Houle C., Dunn J.R., Aye M. (2004). Dimensions and dynamics of residential segregation by income in urban Canada, 1991 1996. Canadian Geographer, 48(4), 433-445. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0008-3658.2004.00069.x
Pendall R. (2005). Does density exacerbate income segregation? Evidence from U.S. Metropolitan areas, 1980 1990. Desegregating The City: Ghettos, Enclaves, and Inequality, 175-199. State University of New York Press.https://doi.org/
Burgess S., Wilson D. (2005). Ethnic segregation in England's schools. Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers, 30(1), 20-36. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-5661.2005.00149.x
Varady D.P. (2005). Desegregating the city: Ghettos, enclaves, and inequality. Desegregating the City: Ghettos, Enclaves, and Inequality, 1-310. State University of New York Press.https://doi.org/
Schmidheiny K. (2006). Income segregation from local income taxation when households differ in both preferences and incomes. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 36(2), 270-299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2005.10.003
Schmidheiny K. (2006). Income segregation and local progressive taxation: Empirical evidence from Switzerland. Journal of Public Economics, 90(3), 429-458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2005.09.003
Schmidheiny K. (2006). Income segregation and local progressive taxation: Empirical evidence from Switzerland. Journal of Public Economics, 90(3), 429-458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2005.09.003
Hodler R., Schmidheiny K. (2006). How fiscal decentralization flattens progressive taxes. FinanzArchiv, 62(2), 281-304. https://doi.org/10.1628/001522106X120695
Reardon S.F., Yun J.T., Kurlaender M. (2006). Implications of income based school assignment policies for racial school segregation. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 28(1), 49-75. https://doi.org/10.3102/01623737028001049
Dawkins C.J. (2007). Space and the measurement of income segregation. Journal of Regional Science, 47(2), 255-272. Blackwell Publishing Inc..https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9787.2007.00508.x
Galbraith J.K., Hale J.T. (2008). State income inequality and presidential election turnout and outcomes. Social Science Quarterly, 89(4), 887-901. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6237.2008.00589.x
Oreopoulos P. (2008). Neighbourhood effects in Canada: A critique. Canadian Public Policy, 34(2), 237-258. https://doi.org/10.3138/cpp.34.2.237
Wood G., Berry M., Taylor E., Nygaard C. (2008). Community mix, affordable housing and metropolitan planning strategy in Melbourne. Built Environment, 34(3), 273-290. https://doi.org/10.2148/benv.34.3.273
Downes T. (2009). School Finance Reform. International Encyclopedia of Education, Third Edition, 216-221. Elsevier.https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-044894-7.01242-2
Watson T. (2009). Inequality and the measurement of residential segregation by income in american neighborhoods. Review of Income and Wealth, 55(3), 820-844. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-4991.2009.00346.x
Watson T. (2009). Inequality and the measurement of residential segregation by income in american neighborhoods. Review of Income and Wealth, 55(3), 820-844. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-4991.2009.00346.x
Dawkins C.J. (2009). Exploring changes in the spatial pattern of income segregation during the 1990s. Research on Economic Inequality, 17(), 159-170. https://doi.org/10.1108/S1049-2585(2009)0000017012
Freeman L. (2009). Neighbourhood diversity, metropolitan segregation and gentrification: What are the links in the US?. Urban Studies, 46(10), 2079-2101. https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098009339426
Rothwell J.T., Massey D.S. (201). Density zoning and class segregation in U.S. metropolitan areas. Social Science Quarterly, 91(5), 1123-1143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6237.2010.00724.x
Wu J. (201). Economic fundamentals and urban suburban disparities. Journal of Regional Science, 50(2), 570-591. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9787.2010.00665.x
Schaltegger C.A., Somogyi F., Sturm J.-E. (2011). Tax competition and income sorting: Evidence from the Zurich metropolitan area. European Journal of Political Economy, 27(3), 455-470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpoleco.2011.01.004
Finney M.M., Goetzke F., Yoon M.J. (2011). Income sorting and the demand for clean air: Evidence from southern California. Land Economics, 87(1), 19-27. University of Wisconsin Press.https://doi.org/10.3368/le.87.1.19
Rey S.J., Folch D.C. (2011). Impact of spatial effects on income segregation indices. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 35(6), 431-441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2011.07.008
Reardon S.F., Bischoff K. (2011). Income inequality and income segregation. American Journal of Sociology, 116(4), 1092-1153. https://doi.org/10.1086/657114
Bayer P., McMillan R. (2012). Tiebout sorting and neighborhood stratification. Journal of Public Economics, 96(11-12), 1129-1143. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2012.02.006
Quillian L. (2012). Segregation and Poverty Concentration: The Role of Three Segregations. American Sociological Review, 77(3), 354-379. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003122412447793
Gauvin L., Vignes A., Nadal J.-P. (2013). Modeling urban housing market dynamics: Can the socio spatial segregation preserve some social diversity?. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 37(7), 1300-1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jedc.2013.03.001
Gauvin L., Vignes A., Nadal J.-P. (2013). Modeling urban housing market dynamics: Can the socio spatial segregation preserve some social diversity?. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 37(7), 1300-1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jedc.2013.03.001
Meltzer R. (2013). Do Homeowners Associations Affect Citywide Segregation? Evidence From Florida Municipalities. Housing Policy Debate, 23(4), 688-713. https://doi.org/10.1080/10511482.2013.812571
Enström Öst C., Söderberg B., Wilhelmsson M. (2014). Household allocation and spatial distribution in a market under ("soft") rent control. Journal of Policy Modeling, 36(2), 353-372. Elsevier.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpolmod.2014.01.002
Walks A. (2014). From Financialization to Sociospatial Polarization of the City? Evidence from Canada. Economic Geography, 90(1), 33-66. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecge.12024
De Fraja G., Martínez-Mora F. (2014). The desegregating effect of school tracking. Journal of Urban Economics, 80(), 164-177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jue.2014.01.001
De Fraja G., Martínez-Mora F. (2014). The desegregating effect of school tracking. Journal of Urban Economics, 80(), 164-177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jue.2014.01.001
Modai-Snir T., Plaut P.O. (2015). Intra metropolitan residential mobility and income sorting trends. Letters in Spatial and Resource Sciences, 8(3), 291-305. Springer Verlag.https://doi.org/10.1007/s12076-014-0133-z
Musterd S., Van Gent W. (2015). Changing welfare context and income segregation in Amsterdam and its metropolitan area. Socio-Economic Segregation in European Capital Cities: East Meets West, 55-79. Taylor and Francis Inc..https://doi.org/
Owens A. (2015). Assisted Housing and Income Segregation among Neighborhoods in U.S. Metropolitan Areas. Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 660(1), 98-116. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0002716215576106
Yang Y., Auchincloss A.H., Rodriguez D.A., Brown D.G., Riolo R., Diez-Roux A.V. (2015). Modeling spatial segregation and travel cost influences on utilitarian walking: Towards policy intervention. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 51(), 59-69. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2015.01.007
Owens A., Reardon S.F., Jencks C. (2016). Income Segregation Between Schools and School Districts. American Educational Research Journal, 53(4), 1159-1197. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831216652722
Williamson P. (2016). Small Area Incomes: Their Spatial Variability and the Relative Efficacy of Proxy, Geodemographic, Imputed and Model Based Estimates. Applied Spatial Analysis and Policy, 9(4), 463-489. Springer Netherlands.https://doi.org/10.1007/s12061-015-9163-1
Andersson R., Hedman L. (2016). Economic decline and residential segregation: a Swedish study with focus on Malmö. Urban Geography, 37(5), 748-768. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/02723638.2015.1133993
Owens A. (2016). Inequality in Children’s Contexts: Income Segregation of Households with and without Children. American Sociological Review, 81(3), 549-574. American Sociological Association.https://doi.org/10.1177/0003122416642430
Quillian L., Lagrange H. (2016). Socioeconomic Segregation in Large Cities in France and the United States. Demography, 53(4), 1051-1084. Springer Science and Business Media, LLC.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-016-0491-9
Agostini C.A., Hojman D., Román A., Valenzuela L. (2016). Income residential segregation in Greater Santiago, 1992 2002: A robust estimation; [Segregación residencial de ingresos en el Gran Santiago, 1992 2002: Una estimación robusta]. Eure, 42(127), 159-184. Revista de Geografia Norte Grande.https://doi.org/10.4067/S0250-71612016000300007
Ruiz-Rivera N., Suárez M., Delgado-Campos J. (2016). Urban segregation and local retail environments. Evidence from Mexico City. Habitat International, 54(), 58-64. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2014.09.001
Wilson W.J. (2016). Black youths, joblessness, and the other side of ‘Black Lives Matter’. Ethnic and Racial Studies, 39(8), 1450-1457. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/01419870.2016.1153689
Lens M.C., Monkkonen P. (2016). Do Strict Land Use Regulations Make Metropolitan Areas More Segregated by Income?. Journal of the American Planning Association, 82(1), 6-21. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/01944363.2015.1111163
Lens M.C., Monkkonen P. (2016). Do Strict Land Use Regulations Make Metropolitan Areas More Segregated by Income?. Journal of the American Planning Association, 82(1), 6-21. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/01944363.2015.1111163
Johnson O.C.A. (2016). Inclusion, exclusion, and the “new” economic inequality. Texas Law Review, 94(7), 1647-1665. School of Law Publications.https://doi.org/
Saporito S. (2017). Shaping Income Segregation in Schools: The Role of School Attendance Zone Geography. American Educational Research Journal, 54(6), 1345-1377. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831217724116
Saporito S. (2017). Shaping Income Segregation in Schools: The Role of School Attendance Zone Geography. American Educational Research Journal, 54(6), 1345-1377. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831217724116
Wolfson M., Gribble S., Beall R. (2017). Exploring Contingent Inequalities: Building the Theoretical Health Inequality Model. Springer Series on Demographic Methods and Population Analysis, 41(), 487-513. Springer Science and Business Media B.V..https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32283-4_17
Iceland J., Hernandez E. (2017). Understanding trends in concentrated poverty: 1980 2014. Social Science Research, 62(), 75-95. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssresearch.2016.09.001
Larson S.J. (2018). Examining the Efficacy of Title VI Social Equity Analysis: A Comparative Case Study of Transit Access and Neighborhood Segregation Outcomes Over Time. Public Integrity, 20(4), 344-357. Taylor and Francis Ltd..https://doi.org/10.1080/10999922.2018.1441595
Garcia-López M.-À., Moreno-Monroy A.I. (2018). Income segregation in monocentric and polycentric cities: Does urban form really matter?. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 71(), 62-79. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2018.05.003
Heilmann K. (2018). Transit access and neighborhood segregation. Evidence from the Dallas light rail system. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 73(), 237-250. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2018.10.007
Bond T.N., Salisbury L. (2018). Local Information, Income Segregation, and Geographic Mobility. B.E. Journal of Economic Analysis and Policy, 18(3), -. De Gruyter.https://doi.org/10.1515/bejeap-2017-0314
Reardon S.F., Bischoff K., Owens A., Townsend J.B. (2018). Has Income Segregation Really Increased? Bias and Bias Correction in Sample Based Segregation Estimates. Demography, 55(6), 2129-2160. Springer Science and Business Media, LLC.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-018-0721-4
Bélec J., Harris R., Rose G. (2018). The Federal Impact on Early Postwar Suburbanization. Housing Policy Debate, 28(6), 854-875. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/10511482.2018.1474124
Logan J.R., Foster A., Ke J., Li F. (2018). The uptick in income segregation: Real trend or random sampling variation?. American Journal of Sociology, 124(1), 185-222. University of Chicago Press.https://doi.org/10.1086/697528
Reardon S.F., Bischoff K. (2018). Income Inequality and Income Segregation. Social Stratification: Class, Race, and Gender in Sociological Perspective, 1023-1034. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429494642-123
Owens A. (2018). Income Segregation between School Districts and Inequality in Students’ Achievement. Sociology of Education, 91(1), 1-27. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0038040717741180
Reardon S.F., Bischoff K. (2018). Income Inequality and Income Segregation. Inequality in the 21st Century: A Reader, 426-435. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429499821-73
Reardon S.F., Bischoff K. (2018). Income Inequality and Income Segregation. Inequality in the 21st Century: A Reader, 426-435. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429499821-73
Li M., Johnson S.B., Newman S., Riley A.W. (2019). Residential mobility and long term exposure to neighborhood poverty among children born in poor families: A U.S. longitudinal cohort study. Social Science and Medicine, 226(), 69-76. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2019.02.042
Pangallo M., Nadal J.-P., Vignes A. (2019). Residential income segregation: A behavioral model of the housing market. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization, 159(), 15-35. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2019.01.010
Pangallo M., Nadal J.-P., Vignes A. (2019). Residential income segregation: A behavioral model of the housing market. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization, 159(), 15-35. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2019.01.010
Taylor K., Anderson J., Frankenberg E. (2019). School and Residential Segregation in School Districts with Voluntary Integration Policies. Peabody Journal of Education, 94(4), 371-387. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/0161956X.2019.1648950
Bischoff K., Owens A. (2019). The Segregation of Opportunity: Social and Financial Resources in the Educational Contexts of Lower and Higher Income Children, 1990 2014. Demography, 56(5), 1635-1664. Springer Science and Business Media, LLC.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-019-00817-y
Galster G., Turner L.M. (2019). Status Aversion, Attraction and Discrepancy as Drivers of Neighborhood Selection. City and Community, 18(3), 937-964. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/cico.12435
Galster G., Turner L.M. (2019). Status Aversion, Attraction and Discrepancy as Drivers of Neighborhood Selection. City and Community, 18(3), 937-964. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/cico.12435
Pearman F.A., II (2019). The Effect of Neighborhood Poverty on Math Achievement: Evidence From a Value Added Design. Education and Urban Society, 51(2), 289-307. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0013124517715066
Christafore D., Leguizamon S. (2019). Neighbourhood inequality spillover effects of gentrification. Papers in Regional Science, 98(3), 1469-1484. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/pirs.12405
Guo C., Buchmann C.M., Schwarz N. (2019). Linking urban sprawl and income segregation Findings from a stylized agent based model. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 46(3), 469-489. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/2399808317719072
Owens A. (2019). Building Inequality: Housing Segregation and Income Segregation. Sociological Science, 6(), -. Society for Sociological Science.https://doi.org/10.15195/v6.a19
Yavaş M. (2019). Dissecting income segregation: Impacts of concentrated affluence on segregation of poverty. Journal of Mathematical Sociology, 43(1), 1-22. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/0022250X.2018.1476858
Sampson R.J. (2019). Neighbourhood effects and beyond: Explaining the paradoxes of inequality in the changing American metropolis. Urban Studies, 56(1), 3-32. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098018795363
Neuman S.B., Moland N. (2019). Book Deserts: The Consequences of Income Segregation on Children’s Access to Print. Urban Education, 54(1), 126-147. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0042085916654525
Wichowsky A. (2019). Civic Life in the Divided Metropolis: Social Capital, Collective Action, and Residential Income Segregation. Urban Affairs Review, 55(1), 257-287. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/1078087416688097
Lasso de la Vega C., Volij O. (202). THE MEASUREMENT OF INCOME SEGREGATION. International Economic Review, 61(4), 1479-1500. Blackwell Publishing Inc..https://doi.org/10.1111/iere.12466
Chetty R., Friedman J.N., Saez E., Turner N., Yagan D. (202). Income Segregation and Intergenerational Mobility across Colleges in the United States. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 135(3), 1567-1633. Oxford University Press.https://doi.org/10.1093/qje/qjaa005
Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. (202). On the link between rail transit and spatial income segregation. Applied Geography, 125(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102364
Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. (202). On the link between rail transit and spatial income segregation. Applied Geography, 125(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102364
Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. (202). On the link between rail transit and spatial income segregation. Applied Geography, 125(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102364
Estep K., Greenberg P. (202). Opting Out: Individualism and Vaccine Refusal in Pockets of Socioeconomic Homogeneity. American Sociological Review, 85(6), 957-991. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0003122420960691
Logan J.R., Foster A., Xu H., Zhang W. (202). Income Segregation: Up or Down, and for Whom?. Demography, 57(5), 1951-1974. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-020-00917-0
Logan J.R., Foster A., Xu H., Zhang W. (202). Income Segregation: Up or Down, and for Whom?. Demography, 57(5), 1951-1974. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13524-020-00917-0
Yabe T., Ukkusuri S.V. (202). Effects of income inequality on evacuation, reentry and segregation after disasters. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 82(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2020.102260
Ziller C., Spörlein C. (202). Residential Segregation and Social Trust of Immigrants and Natives: Evidence From the Netherlands. Frontiers in Sociology, 5(), -. Frontiers Media S.A..https://doi.org/10.3389/fsoc.2020.00045
Haddad M.A. (202). Residential income segregation and commuting in a Latin American city. Applied Geography, 117(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102186
Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. (202). Impact of new rail transit stations on neighborhood destination choices and income segregation. Cities, 102(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2020.102737
Sampson R.J., Levy B.L. (202). Beyond Residential Segregation: Mobility Based Connectedness and Rates of Violence in Large Cities. Race and Social Problems, 12(1), 77-86. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s12552-019-09273-0
Owens A. (202). Unequal Opportunity: School and Neighborhood Segregation in the USA. Race and Social Problems, 12(1), 29-41. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s12552-019-09274-z
Drouhot L.G. (202). Income Segregation and the Incomplete Integration of Islam in the Paris Metropolitan Area. Socius, 6(), -. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/2378023119899585
Richards M.P., Stroub K.J. (202). Metropolitan public school district segregation by race and income, 2000 2011. Teachers College Record, 122(5), 21-41. Teachers College, Columbia University.https://doi.org/
Havewala F. (2021). The dynamics between the food environment and residential segregation: An analysis of metropolitan areas. Food Policy, 103(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2020.102015
Gallagher R.M. (2021). Income segregation's impact on local public expenditures: Evidence from municipalities and school districts, 1980 2010. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 90(), -. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2021.103710
Gallagher R.M. (2021). Income segregation's impact on local public expenditures: Evidence from municipalities and school districts, 1980 2010. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 90(), -. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2021.103710
Gallagher R.M. (2021). Income segregation's impact on local public expenditures: Evidence from municipalities and school districts, 1980 2010. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 90(), -. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2021.103710
Delmelle E., Nilsson I., Adu P. (2021). Poverty suburbanization, job accessibility, and employment outcomes. Social Inclusion, 9(2), 166-178. Cogitatio Press.https://doi.org/10.17645/si.v9i2.3735
Park H. (2021). Income sorting by specialized services: Service differentiation by overlapping governments. Social Science Quarterly, 102(6), 2761-2775. John Wiley and Sons Inc.https://doi.org/10.1111/ssqu.13078
Taylor K., Frankenberg E. (2021). Student Assignment Policies and Racial and Income Segregation of Schools, School Attendance Zones, and Neighborhoods. Educational Administration Quarterly, 57(5), 747-775. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/0013161X211024720
Zhang T., Duan X., Wong D.W.S., Lu Y. (2021). Discovering income economic segregation patterns: A residential mobility embedding approach. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 90(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2021.101709
Mehta A. (2021). SALT, Subsidies, and Subnational Spending. Columbia Journal of Law and Social Problems, 54(2), 219-260. Columbia Law Review Association.https://doi.org/
Modai-Snir T. (2021). Increasing Inequality and the Changing Spatial Distribution of Income in Tel Aviv. Urban Book Series, 191-207. Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64569-4_10
Veneri P., Comandon A., Garcia-López M.-À., Daams M.N. (2021). What do divided cities have in common? An international comparison of income segregation. Journal of Regional Science, 61(1), 162-188. Blackwell Publishing Inc..https://doi.org/10.1111/jors.12506
Ismail M., Warsame A., Wilhelmsson M. (2021). Do segregated housing markets have a spillover effect on housing prices in nearby residential areas?. Journal of European Real Estate Research, 14(2), 169-186. Emerald Group Holdings Ltd..https://doi.org/10.1108/JERER-06-2020-0037
Santos M.I.D., Santos G.F.D., Freitas A., Sousa Filho J.F.D., Castro C., Paiva A.S.S., Friche A.A.D.L., Barber S., Caiaffa W.T., Barreto M.L. (2021). Urban income segregation and homicides: An analysis using Brazilian cities selected by the Salurbal project. SSM - Population Health, 14(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssmph.2021.100819
Santos M.I.D., Santos G.F.D., Freitas A., Sousa Filho J.F.D., Castro C., Paiva A.S.S., Friche A.A.D.L., Barber S., Caiaffa W.T., Barreto M.L. (2021). Urban income segregation and homicides: An analysis using Brazilian cities selected by the Salurbal project. SSM - Population Health, 14(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssmph.2021.100819
Kulkarni N., Malmendier U. (2022). Homeownership segregation. Journal of Monetary Economics, 129(), 123-149. Elsevier B.V..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmoneco.2022.05.001
Wessel T. (2022). Business Services, Income Inequality, and Income Segregation in Metropolitan Areas: Direct and Indirect Links. Economic Geography, 98(5), 464-486. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/00130095.2022.2074831
Peters S.J., Carter J.S., III (2022). Predictors of Access to Gifted Education: What Makes for a Successful School?. Exceptional Children, 88(4), 341-358. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/00144029221081092
Kim Y., Colabianchi N. (2022). The Longitudinal Effect of Area Socioeconomic Changes on Obesity: a Longitudinal Cohort Study in the USA from 2003 to 2017. Journal of Urban Health, 99(6), 1068-1079. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11524-022-00681-z
Ekenga C.C., Tian R. (2022). Promoting Food Equity in the Context of Residential Segregation. Environmental Justice, 15(6), 346-351. Mary Ann Liebert Inc..https://doi.org/10.1089/env.2021.0029
Schachner J.N. (2022). Neighborhood Economic Change in an Era of Metropolitan Divergence. Urban Affairs Review, 58(4), 923-959. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/10780874211016940
Schachner J.N. (2022). Neighborhood Economic Change in an Era of Metropolitan Divergence. Urban Affairs Review, 58(4), 923-959. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/10780874211016940
Ng M.K.M., Roper J., Lee C.L., Pettit C. (2022). The Reflection of Income Segregation and Accessibility Cleavages in Sydney’s House Prices. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(7), -. MDPI.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11070413
Ng M.K.M., Roper J., Lee C.L., Pettit C. (2022). The Reflection of Income Segregation and Accessibility Cleavages in Sydney’s House Prices. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(7), -. MDPI.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11070413
Dalane K., Marcotte D.E. (2022). The Segregation of Students by Income in Public Schools. Educational Researcher, 51(4), 245-254. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X221081853
Beaubrun-Diant K., Maury T.-P. (2022). On the Impact of Public Housing on Income Segregation in France. Demography, 59(2), 685-706. Duke University Press.https://doi.org/10.1215/00703370-9807596
Quick M., Revington N. (2022). Exploring the global and local patterns of income segregation in Toronto, Canada: A multilevel multigroup modeling approach. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 49(2), 637-653. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/23998083211021419
Quick M., Revington N. (2022). Exploring the global and local patterns of income segregation in Toronto, Canada: A multilevel multigroup modeling approach. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 49(2), 637-653. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/23998083211021419
Won J. (2022). Exploring Spatial Clustering Over Time and Spillover Effects of the Low Income Housing Tax Credit on Neighborhood Level Income Segregation. Urban Affairs Review, 58(3), 799-831. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/1078087420973436
Kim H., Schmidt N.M., Osypuk T.L., Thyden N., Rehkopf D. (2022). Effects of housing vouchers on the long term exposure to neighbourhood opportunity among low income families: the moving to opportunity experiment. Housing Studies, 38(1), 128-151. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/02673037.2022.2112154
Adu P., Delmelle E.C. (2022). Spatial Variations in Exclusionary Criteria from Online Rental Advertisements. Professional Geographer, 74(4), 704-714. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/00330124.2022.2061537
South S.J., Huang Y., Spring A. (2022). Proximate sources of growth in neighborhood income segregation: Class selective migration versus in situ change. Social Science Research, 101(), -. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssresearch.2021.102624
