Age segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
[[File:age_segregation.png|780x780px]] | [[File:age_segregation.png|780x780px]] | ||
This visualization is based on the study [[How_to_cite_Segregation_Wiki| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of | For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | ||
* | * [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | ||
* | * [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | ||
* | * [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | ||
* | * [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
Revision as of 07:48, 10 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1]
1978
United States
Definition
Age segregation refers to the separation of individuals of different age groups or generations in various aspects of life, such as housing, education, social activities, and work. This segregation can occur intentionally or unintentionally, and it may have both positive and negative implications.
Some argue that age segregation can foster a sense of community and provide opportunities for individuals to interact with peers who share similar life experiences and challenges. For example, senior living communities often provide a supportive environment for older adults to socialize and engage in activities tailored to their needs.
However, age segregation can also lead to isolation and limited social interaction among different age groups. This can result in a lack of understanding and empathy between generations, as well as missed opportunities for intergenerational learning and support.
Overall, while age segregation may have some benefits in certain contexts, it is important to consider how it impacts social cohesion and opportunities for meaningful connections across age groups. Efforts to promote intergenerational interactions and understanding can help counteract the negative effects of age segregation.
See also
Related segregation forms
Age segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
social segregation, residential segregation, gender segregation, racial segregation, occupational segregation, educational segregation, urban segregation, neighborhood segregation, age neighborhood segregation
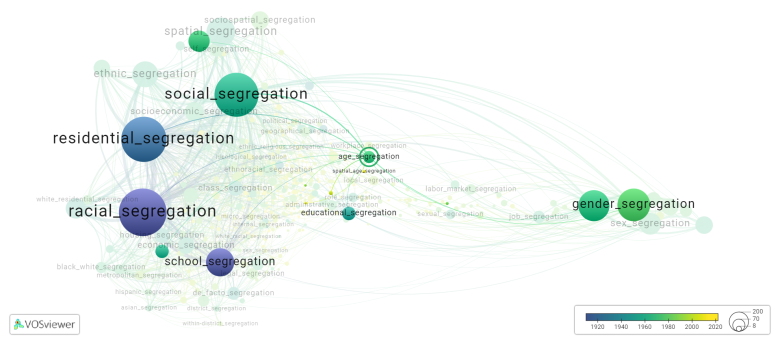
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References
Notes
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Age segregation appears in the following literature
Garbarino J., Burston N., Raber S., Russell R., Crouter A. (1978). The social maps of children approaching adolescence: Studying the ecology of youth development. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 7(4), 417-428. Kluwer Academic Publishers-Plenum Publishers.https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01537809
Coleman J.C. (1979). Who leads who astray? Causes of anti social behaviour in adolescence. Journal of Adolescence, 2(3), 179-185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-1971(79)80010-X
Montemayor R., Van Komen R. (198). Age segregation of adolescents in and out of school. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 9(5), 371-381. Kluwer Academic Publishers-Plenum Publishers.https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02087675
Lagory M., Ward R., Juravich T. (198). The Age Segregation Process: Explanation for American Cities. Urban Affairs Review, 16(1), 59-80. https://doi.org/10.1177/107808748001600104
Lagory M., Ward R., Juravich T. (198). The Age Segregation Process: Explanation for American Cities. Urban Affairs Review, 16(1), 59-80. https://doi.org/10.1177/107808748001600104
Conger J.J. (1981). Freedom and commitment: Families, youth, and social change. American Psychologist, 36(12), 1475-1484. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.36.12.1475
Ellis S., Rogoff B., Cromer C.C. (1981). Age segregation in children's social interactions. Developmental Psychology, 17(4), 399-407. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.17.4.399
Gory M.L., Ward R.A., Mucatel M. (1981). Patterns of age segregation. Sociological Focus, 14(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380237.1981.10570378
Blyth D.A., Hill J.P., Thiel K.S. (1982). Early adolescents' significant others: Grade and gender differences in perceived relationships with familial and nonfamilial adults and young people. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 11(6), 425-450. Kluwer Academic Publishers-Plenum Publishers.https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01538805
Chevan A. (1982). Age, housing choice, and neighborhood age structure.. American Journal of Sociology, 87(5), 1133-1149. https://doi.org/10.1086/227558
Deimling G., Harel Z., Noelker L. (1983). Racial differences in social integration and life satisfaction among aged public housing residents. International Journal of Aging and Human Development, 17(3), 203-212. https://doi.org/10.2190/4QHN-EKBF-N7L0-9UD3
Wister A.V. (1985). Living Arrangement Choices among the Elderly. Canadian Journal on Aging / La Revue canadienne du vieillissement, 4(3), 127-144. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0714980800015968
Moore H.A., Ollenburger J.C. (1986). What Sex is Your Parachute?: Interest inventory/counseling models and the perpetuation of the sex/wage segregation of the labor market. Work and Occupations, 13(4), 511-531. https://doi.org/10.1177/0730888486013004004
OKRAKU I.O. (1987). Age residential segregation in Canadian cities. Canadian Review of Sociology/Revue canadienne de sociologie, 24(3), 431-452. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-618X.1987.tb01105.x
Allen J.P. (1989). Social Impact of Age Mixing and Age Segregation in School: A Context Sensitive Investigation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 81(3), 408-416. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.81.3.408
Nakagawa S. (199). Changing Segregation Patterns by Age Group in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area From the Viewpoint of Migration with Cohort Analysis. Geographical review of Japan, Series B., 63(1), 34-47. https://doi.org/10.4157/grj1984b.63.34
Imhoff G. (199). The Position of U.S. English on Bilingual Education. The ANNALS of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 508(1), 48-61. https://doi.org/10.1177/0002716290508001005
Donato R., Garcia H. (1991). Language segregation in desegregated schools:A question of equity. Equity and Excellence in Education, 25(2-4), 94-99. https://doi.org/10.1080/1066568910250214
Brinton M.C., Ngo H.-Y. (1993). Age and sex in the occupational structure: A United States Japan comparison. Sociological Forum, 8(1), 93-111. Kluwer Academic Publishers-Plenum Publishers.https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01112332
Rose M. (1998). Snow Belt: Retirement communties past, present, and future. Plan Canada, 38(4), 19-22. https://doi.org/
Smith G.C. (1998). Change in elderly residential segregation in Canadian metropolitan areas, 1981 91. Canadian Journal on Aging, 17(1), 59-82. Cambridge University Press.https://doi.org/10.1017/S0714980800010357
Percival J. (2001). Self esteem and social motivation in age segregated settings. Housing Studies, 16(6), 827-840. https://doi.org/10.1080/02673030120090566
Rogoff B., Angelillo C. (2002). Investigating the coordinated functioning of multifaceted cultural practices in human development. Human Development, 45(4), 211-225. https://doi.org/10.1159/000064981
Rogoff B., Paradise R., Arauz R.M., Correa-Chávez M., Angelillo C. (2003). Firsthand Learning through Intent Participation. Annual Review of Psychology, 54(), 175-203. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.54.101601.145118
Dickerson B., Watkins D.R. (2003). The caleb affect: The oldest old in church and society. Journal of Religious Gerontology, 15(1-2), 201-213. https://doi.org/10.1300/J078v15n01_15
Uhlenberg P., De Jong Gierveld J. (2004). Age segregation in later life: An examination of personal networks. Ageing and Society, 24(1), 5-28. Cambridge University Press.https://doi.org/10.1017/S0144686X0300151X
Cameron R. (2005). Aging and gendering. Language in Society, 34(1), 23-61. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0047404505050025
Hirsch A.R. (2005). Review Essay: Whose “Golden Age” of Segregation?. Journal of Urban History, 31(4), 537-545. https://doi.org/10.1177/0096144204274390
Hagestad G.O., Uhlenberg P. (2005). The social separation of old and young: A root of ageism. Journal of Social Issues, 61(2), 343-360. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-4560.2005.00409.x
Hagestad G.O., Uhlenberg P. (2006). Should we be concerned about age segregation? Some theoretical and empirical explorations. Research on Aging, 28(6), 638-653. https://doi.org/10.1177/0164027506291872
Hagestad G.O., Uhlenberg P. (2006). Should we be concerned about age segregation? Some theoretical and empirical explorations. Research on Aging, 28(6), 638-653. https://doi.org/10.1177/0164027506291872
Hagestad G.O., Uhlenberg P. (2006). Should we be concerned about age segregation? Some theoretical and empirical explorations. Research on Aging, 28(6), 638-653. https://doi.org/10.1177/0164027506291872
Gierveld J.D.J., Hagestad G.O. (2006). Perspectives on the integration of older men and women. Research on Aging, 28(6), 627-637. https://doi.org/10.1177/0164027506291871
Manis A.M. (2006). The beginnings of interracialism: Macon, Georgia, in the 1930s. History and Hope in the Heart of Dixie: Scholarship, Activism, and Wayne Flynt in the Modern South, 91-123. The University of Alabama Press.https://doi.org/
MacLean A. (2006). Age stratification at work: Trends in occupational age segregation in the United States, 1950 2000. Research in Social Stratification and Mobility, 24(3), 299-310. JAI Press.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rssm.2005.08.001
MacLean A. (2006). Age stratification at work: Trends in occupational age segregation in the United States, 1950 2000. Research in Social Stratification and Mobility, 24(3), 299-310. JAI Press.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rssm.2005.08.001
Prescott L.E. (2007). Journeying through Jim Crow: Spanish American Travelers in the United States during the age of segregation. Latin American Research Review, 42(1), 3-28. University of Texas Press.https://doi.org/10.1353/lar.2007.0010
Jonda B. (2008). How do local politicians see the situation of older people in East and West Germany?. The Ageing Societies of Central and Eastern Europe: Some Problems - Some Solutions, 127-141. Jagiellonian University Press.https://doi.org/
Addae-Dapaah K. (2008). Age segregation and the quality of life of the elderly people in studio apartments. Journal of Housing for the Elderly, 22(1-2), 127-161. https://doi.org/10.1080/02763890802097151
McCann R.J., Trokhimtchouk M. (2009). Optimal partition of a large labor force into working pairs. Economic Theory, 42(2), 375-395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00199-008-0420-2
Uhlenberg P. (2009). Children in an aging society. Journals of Gerontology - Series B Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 64(4), 489-496. Gerontological Society of America.https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/gbp001
Kerbs J.J., Jolley J.M. (2009). A commentary on age segregation for older prisoners: Philosophical and pragmatic considerations for correctional systems. Criminal Justice Review, 34(1), 119-139. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734016808324245
Kelly H. (201). Race, remembering, and Jim Crow's teachers. Race, Remembering, and Jim Crow's Teachers, 1-154. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203852354
Rogoff B., Morelli G.A., Chavajay P. (201). Children's integration in communities and segregation from people of differing ages. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 5(4), 431-440. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691610375558
Cook L.D. (2012). Overcoming discrimination by consumers during the age of segregation: The example of Garrett Morgan. Business History Review, 86(2), 211-234. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007680512000372
Winkler R., Klaas R. (2012). Residential segregation by age in the United States. Journal of Maps, 8(4), 374-378. https://doi.org/10.1080/17445647.2012.739099
Castelló X., Loureiro-Porto L., Miguel M.S. (2013). Agent based models of language competition. International Journal of the Sociology of Language, 21-51. Walter de Gruyter GmbH.https://doi.org/10.1515/ijsl-2013-0022
Winkler R. (2013). Research Note: Segregated by Age: Are We Becoming More Divided?. Population Research and Policy Review, 32(5), 717-727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11113-013-9291-8
Hashemi Nazari S.S., Mahmoodi M., Mansournia M.-A., Holakouie Naieni K. (2013). Association of residential segregation and disability: A multilevel study using Iranian census data. Journal of Urban Health, 90(1), 67-82. Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11524-012-9705-7
Luo B., Zhou K., Jin E.J., Newman A., Liang J. (2013). Ageism among College Students: A Comparative Study between U.S. and China. Journal of Cross-Cultural Gerontology, 28(1), 49-63. Springer Science and Business Media, LLC.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10823-013-9186-5
Kump S., Krašovec S.J. (2014). Intergenerational learning in different contexts. Learning Across Generations in Europe: Contemporary Issues in Older Adult Education, 167-177. Sense Publishers.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-6209-902-9_14
Corvalan A., Vargas M. (2015). Segregation and conflict: An empirical analysis. Journal of Development Economics, 116(), 212-222. Elsevier.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdeveco.2015.05.002
Brasington D.M., Hite D., Jauregui A. (2015). House price impacts of racial, income, education, and age neighborhood segregation. Journal of Regional Science, 55(3), 442-467. https://doi.org/10.1111/jors.12173
Kerbs J.J., Jolley J.M., Kanaboshi N. (2015). The interplay between law and social science in the age segregation debate. Journal of Crime and Justice, 38(1), 77-95. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/0735648X.2014.894856
Puhakka R., Poikolainen J., Karisto A. (2015). Spatial Practises and Preferences of Older and Younger People: Findings from the Finnish Studies. Journal of Social Work Practice, 29(1), 69-83. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/02650533.2014.993948
Carrington P.J. (2016). Gender and Age Segregation and Stratification in Criminal Collaborations. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 32(4), 613-649. Springer New York LLC.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10940-015-9269-2
Dannefer D., Feldman K. (2017). Age integration, age segregation, and Generation X: Life course perspectives. Generations, 41(3), 20-26. American Society on Aging.https://doi.org/
(2017). The youth ghetto: Age segregation and conflict in the American sixties (1968). Protest: Studies of Collective Behaviour and Social Movements, 71-88. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315127583
Demas L. (2017). Game of privilege: An African American history of golf. Game of Privilege: An African American History of Golf, 1-363. University of North Carolina Press.https://doi.org/
Haddad G.J. (2017). Understanding women entrepreneurial motivations: Does age matter?. Lebanon: Social, Political and Economic Issues, 65-84. Nova Science Publishers, Inc..https://doi.org/
Sabater A., Graham E., Finney N. (2017). The spatialities of ageing: Evidencing increasing spatial polarisation between older and younger adults in England and Wales. Demographic Research, 36(1), 731-744. Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research.https://doi.org/10.4054/DemRes.2017.36.25
Sabater A., Graham E., Finney N. (2017). The spatialities of ageing: Evidencing increasing spatial polarisation between older and younger adults in England and Wales. Demographic Research, 36(1), 731-744. Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research.https://doi.org/10.4054/DemRes.2017.36.25
Siedentop S., Zakrzewski P., Stroms P. (2018). A childless urban renaissance? Age selective patterns of population change in north american and german metropolitan areas. Regional Studies, Regional Science, 5(1), 1-20. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/21681376.2017.1412270
Oliver C., Blythe M., Roe J. (2018). Negotiating sameness and difference in geographies of older age. Area, 50(4), 444-451. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1111/area.12429
Deng G., Mao L. (2018). Spatially explicit age segregation index and self rated health of older adults in US cities. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 7(9), -. MDPI AG.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7090351
Deng G., Mao L. (2018). Spatially explicit age segregation index and self rated health of older adults in US cities. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 7(9), -. MDPI AG.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7090351
Deng G., Mao L. (2018). Spatially explicit age segregation index and self rated health of older adults in US cities. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 7(9), -. MDPI AG.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7090351
Rajendran P. (2018). A study of age related work motivation. Medico-Legal Update, 18(1), 418-420. World Informations Syndicate.https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-1283.2018.00084.1
Elliott O'Dare C., Timonen V., Conlon C. (2019). Intergenerational friendships of older adults: why do we know so little about them?. Ageing and Society, 39(1), 1-16. Cambridge University Press.https://doi.org/10.1017/S0144686X17000800
Filinson R., Ciambrone D. (2019). “Trying to blend in, what else can we do?” Intergenerational relationships among aged inmates: Research. Journal of Intergenerational Relationships, 17(1), 74-92. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/15350770.2018.1500328
Sun H., Schafer M.H. (2019). Age integration in older Europeans’ non kin core networks: Does formal social participation play a role?. European Journal of Ageing, 16(4), 455-472. Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10433-019-00507-z
Santiago M. (2019). Historical Inquiry to Challenge the Narrative of Racial Progress. Cognition and Instruction, 37(1), 93-117. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/07370008.2018.1539734
Scott D. (202). Intergenerationality, family narratives, and black geographic space in rural North Carolina. Gender, Place and Culture, 27(7), 984-1006. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/0966369X.2019.1612854
Revington N., August M. (202). Making a market for itself: The emergent financialization of student housing in Canada. Environment and Planning A, 52(5), 856-877. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0308518X19884577
Lamar M., Lerner A.J., James B.D., Yu L., Glover C.M., Wilson R.S., Barnes L.L. (202). Relationship of early life residence and educational experience to level and change in cognitive functioning: Results of the minority aging research study. Journals of Gerontology - Series B Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 75(7), E81-E92. Gerontological Society of America.https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/gbz031
Fried L.P. (202). Designing a new social infrastructure to combat loneliness in aging adults. Generations, 44(3), -. American Society on Aging.https://doi.org/
Kleijberg M., Ahlberg B.M., Macdonald A., Lindqvist O., Tishelman C. (2021). Navigating power dynamics in engaging communities in end of life issues Lessons learned from developing community based intergenerational arts initiatives about death and loss. Death Studies, 45(8), 651-664. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/07481187.2019.1671547
Steward A., McDevitt K. (2021). “Otherwise We Would Be like an Island”: A Phenomenological Understanding of Intergenerational Engagement Aimed at Reducing Social Isolation. Journal of Intergenerational Relationships, -. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/15350770.2021.1997870
Revington N. (2021). Age Segregation, Intergenerationality, and Class Monopoly Rent in the Student Housing Submarket. Antipode, 53(4), 1228-1250. John Wiley and Sons Inc.https://doi.org/10.1111/anti.12710
Lichtenstein B. (2021). From "coffin Dodger" to "boomer Remover": Outbreaks of Ageism in Three Countries with Divergent Approaches to Coronavirus Control. Journals of Gerontology - Series B Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 76(4), E206-E212. Gerontological Society of America.https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/gbaa102
Astapova A. (2022). An Estonian Russian Language Club as a Venue for Grassroots Ethnic Integration. Nationalities Papers, 50(3), 498-514. Cambridge University Press.https://doi.org/10.1017/nps.2021.8
Das Gupta D., Wong D.W.S. (2022). Changing Age Segregation in the US: 1990 to 2010. Research on Aging, 44(9-10), 669-681. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/01640275221074398
Cohn-Schwartz E., Schafer M.H., Ayalon L. (2022). Age integration in later life social networks and self perceptions of aging: examining their reciprocal associations. European Journal of Ageing, 19(4), 1145-1153. Springer Science and Business Media B.V..https://doi.org/10.1007/s10433-022-00688-0
Milias V., Psyllidis A. (2022). Measuring spatial age segregation through the lens of co accessibility to urban activities. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 95(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2022.101829
Milias V., Psyllidis A. (2022). Measuring spatial age segregation through the lens of co accessibility to urban activities. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 95(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2022.101829
Sabater A., Finney N. (2022). Age segregation and housing unaffordability: Generational divides in housing opportunities and spatial polarisation in England and Wales. Urban Studies, -. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/00420980221121088
Sabater A., Finney N. (2022). Age segregation and housing unaffordability: Generational divides in housing opportunities and spatial polarisation in England and Wales. Urban Studies, -. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/00420980221121088
