Metropolitan income segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===== Date and country of first publication<ref>Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).</ref>===== | |||
2020<br> | 2020<br> | ||
United States | |||
===== Definition ===== | |||
Metropolitan income segregation refers to the unequal distribution of income levels among different neighborhoods or areas within a metropolitan area. This can result in certain neighborhoods being predominantly made up of either high-income or low-income residents, leading to socioeconomic disparities and limited opportunities for upward mobility for individuals residing in low-income areas. Income segregation can also impact access to quality education, healthcare, and other essential services, creating a cycle of poverty and inequality within the metropolitan area. Efforts to address income segregation may involve policies that promote affordable housing, transportation options, and economic development in order to create more inclusive and equitable communities. | Metropolitan income segregation refers to the unequal distribution of income levels among different neighborhoods or areas within a metropolitan area. This can result in certain neighborhoods being predominantly made up of either high-income or low-income residents, leading to socioeconomic disparities and limited opportunities for upward mobility for individuals residing in low-income areas. Income segregation can also impact access to quality education, healthcare, and other essential services, creating a cycle of poverty and inequality within the metropolitan area. Efforts to address income segregation may involve policies that promote affordable housing, transportation options, and economic development in order to create more inclusive and equitable communities. | ||
===== Synonyms ===== | |||
The following terms are synonymous with metropolitan income segregation: | |||
metro income segregation. | |||
References and literature addressing this segregation form under these synonymous terms can be found below. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
==Related segregation forms== | |||
Metropolitan income segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms: | |||
[[social segregation]], [[income segregation]], [[spatial income segregation]], [[residential segregation]] | |||
[[File:metropolitan_income_segregation.png|780x780px]] | |||
This visualization is based on the study [[Segregation_Wiki:About| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
== | ==Notes== | ||
<references /> | |||
{{NoteAI}} | |||
==Metropolitan income segregation appears in the following literature== | |||
Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. (202). On the link between rail transit and spatial income segregation. ''Applied Geography'', ''125''(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102364 | |||
Schachner J.N. (2022). Neighborhood Economic Change in an Era of Metropolitan Divergence. ''Urban Affairs Review'', ''58''(4), 923-959. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/10780874211016940 | |||
Latest revision as of 07:17, 16 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1][edit | edit source]
2020
United States
Definition[edit | edit source]
Metropolitan income segregation refers to the unequal distribution of income levels among different neighborhoods or areas within a metropolitan area. This can result in certain neighborhoods being predominantly made up of either high-income or low-income residents, leading to socioeconomic disparities and limited opportunities for upward mobility for individuals residing in low-income areas. Income segregation can also impact access to quality education, healthcare, and other essential services, creating a cycle of poverty and inequality within the metropolitan area. Efforts to address income segregation may involve policies that promote affordable housing, transportation options, and economic development in order to create more inclusive and equitable communities.
Synonyms[edit | edit source]
The following terms are synonymous with metropolitan income segregation:
metro income segregation.
References and literature addressing this segregation form under these synonymous terms can be found below.
See also[edit | edit source]
Related segregation forms[edit | edit source]
Metropolitan income segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
social segregation, income segregation, spatial income segregation, residential segregation
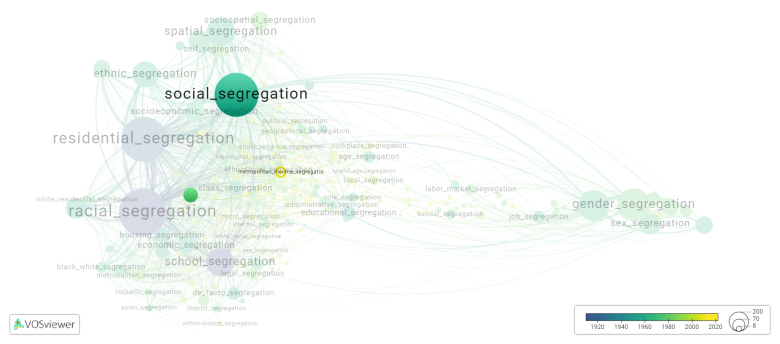
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References[edit | edit source]
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Metropolitan income segregation appears in the following literature[edit | edit source]
Nilsson I., Delmelle E.C. (202). On the link between rail transit and spatial income segregation. Applied Geography, 125(), -. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102364
Schachner J.N. (2022). Neighborhood Economic Change in an Era of Metropolitan Divergence. Urban Affairs Review, 58(4), 923-959. SAGE Publications Inc..https://doi.org/10.1177/10780874211016940
