Hyper segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===== Date and country of first publication<ref>Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).</ref>===== | |||
2006<br> | 2006<br> | ||
United States | United States | ||
===== Definition ===== | |||
Hyper segregation is a term used to describe extreme levels of racial and economic segregation in a particular area. This typically involves the concentration of a specific racial or economic group in certain neighborhoods or areas, leading to limited social interaction and opportunities for residents of different backgrounds. Hyper segregation is often associated with systemic discrimination and inequality, resulting in disparities in access to resources, services, and opportunities for marginalized communities. | Hyper segregation is a term used to describe extreme levels of racial and economic segregation in a particular area. This typically involves the concentration of a specific racial or economic group in certain neighborhoods or areas, leading to limited social interaction and opportunities for residents of different backgrounds. Hyper segregation is often associated with systemic discrimination and inequality, resulting in disparities in access to resources, services, and opportunities for marginalized communities. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
==Related segregation forms== | |||
Hyper segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms: | |||
[[residential segregation]], [[ethnic segregation]], [[multigroup segregation]], [[status segregation]], [[socioeconomic segregation]], [[racial segregation]] | |||
[[File:hyper_segregation.png|780x780px]] | |||
This visualization is based on the study [[Segregation_Wiki:About| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
== | {{NoteAI}} | ||
==Hyper segregation appears in the following literature== | |||
Fossett M. (2006) | Fossett M. (2006). Ethnic preferences, social distance dynamics, and residential segregation: Theoretical explorations using simulation analysis. ''Journal of Mathematical Sociology'', ''30''(3-4), 185-273. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222500500544052 | ||
Marmolejo-Duartey C. | Marmolejo-Duartey C., Batista-DóRia de Souza N.J. (2011). Urban conditions and socioeconomic segregation: An analysis for Maceió Alagoas, Brazil; [Estructura urbana y segregación socioresidencial: Un análisis para Maceió Alagoas, Brasil]. ''Papeles de Poblacion'', ''17''(70), 247-286. https://doi.org/ | ||
Curley A.M. (2016) | Curley A.M. (2016). A New Place, a New Network? Social Capital Effects of Residential Relocation for Poor Women. ''Networked Urbanism: Social Capital in the City'', 85-103. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315597805-7 | ||
Carhill-Poza A. (2017) | Carhill-Poza A. (2017). “If you don't find a friend in here, it's gonna be hard for you”: Structuring bilingual peer support for language learning in urban high schools. ''Linguistics and Education'', ''37''(), 63-72. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.linged.2016.09.001 | ||
Weffer S.E. (2017) | Weffer S.E. (2017). Are the Truly Disadvantaged Truly Demobilized? Neighborhood Disadvantage and Protest in Chicago, 1970 1990. ''Critical Sociology'', ''43''(2), 267-289. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0896920515623074 | ||
Hendrickson C.S. (2018) | Hendrickson C.S. (2018). Ending racial profiling in the church: Revisiting the homogenous unit principle. ''Mission Studies'', ''35''(3), 342-365. Brill Academic Publishers.https://doi.org/10.1163/15733831-12341589 | ||
del Pulgar C.P. (2021) | del Pulgar C.P. (2021). DISMANTLING THE JUST CITY: The unevenness of green experiences in Amsterdam Noord. ''The Green City and Social Injustice: 21 Tales from North America and Europe'', 35-48. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003183273-3 | ||
Johnson J.H., Jr. | Johnson J.H., Jr., Bonds J.M., Parnell A.M., Bright C.M. (2021). Coronavirus Vaccine Distribution: Moving to a Race Conscious Approach for a Racially Disparate Problem. ''Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities'', ''8''(4), 799-802. Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH.https://doi.org/10.1007/s40615-021-01051-2 | ||
Bell M. (2021) | Bell M. (2021). The Color Line and the Classroom: Racialized Space and the Making of Neoliberal Schools. ''Political Economy: Theories, Principles and Politics'', 191-213. Nova Science Publishers, Inc..https://doi.org/ | ||
Latest revision as of 07:17, 16 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1][edit | edit source]
2006
United States
Definition[edit | edit source]
Hyper segregation is a term used to describe extreme levels of racial and economic segregation in a particular area. This typically involves the concentration of a specific racial or economic group in certain neighborhoods or areas, leading to limited social interaction and opportunities for residents of different backgrounds. Hyper segregation is often associated with systemic discrimination and inequality, resulting in disparities in access to resources, services, and opportunities for marginalized communities.
See also[edit | edit source]
Related segregation forms[edit | edit source]
Hyper segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
residential segregation, ethnic segregation, multigroup segregation, status segregation, socioeconomic segregation, racial segregation
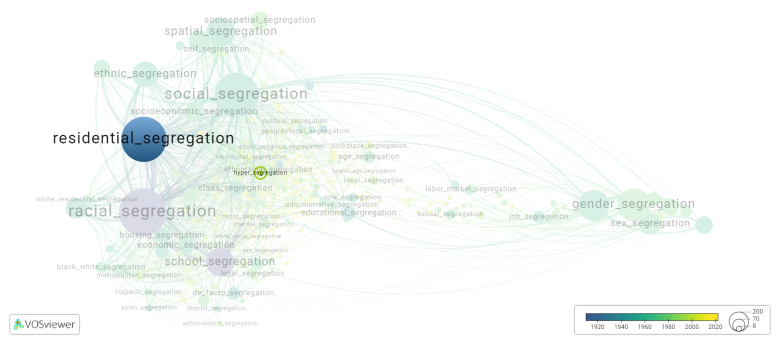
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References[edit | edit source]
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Hyper segregation appears in the following literature[edit | edit source]
Fossett M. (2006). Ethnic preferences, social distance dynamics, and residential segregation: Theoretical explorations using simulation analysis. Journal of Mathematical Sociology, 30(3-4), 185-273. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222500500544052
Marmolejo-Duartey C., Batista-DóRia de Souza N.J. (2011). Urban conditions and socioeconomic segregation: An analysis for Maceió Alagoas, Brazil; [Estructura urbana y segregación socioresidencial: Un análisis para Maceió Alagoas, Brasil]. Papeles de Poblacion, 17(70), 247-286. https://doi.org/
Curley A.M. (2016). A New Place, a New Network? Social Capital Effects of Residential Relocation for Poor Women. Networked Urbanism: Social Capital in the City, 85-103. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315597805-7
Carhill-Poza A. (2017). “If you don't find a friend in here, it's gonna be hard for you”: Structuring bilingual peer support for language learning in urban high schools. Linguistics and Education, 37(), 63-72. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.linged.2016.09.001
Weffer S.E. (2017). Are the Truly Disadvantaged Truly Demobilized? Neighborhood Disadvantage and Protest in Chicago, 1970 1990. Critical Sociology, 43(2), 267-289. SAGE Publications Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1177/0896920515623074
Hendrickson C.S. (2018). Ending racial profiling in the church: Revisiting the homogenous unit principle. Mission Studies, 35(3), 342-365. Brill Academic Publishers.https://doi.org/10.1163/15733831-12341589
del Pulgar C.P. (2021). DISMANTLING THE JUST CITY: The unevenness of green experiences in Amsterdam Noord. The Green City and Social Injustice: 21 Tales from North America and Europe, 35-48. Taylor and Francis.https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003183273-3
Johnson J.H., Jr., Bonds J.M., Parnell A.M., Bright C.M. (2021). Coronavirus Vaccine Distribution: Moving to a Race Conscious Approach for a Racially Disparate Problem. Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities, 8(4), 799-802. Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH.https://doi.org/10.1007/s40615-021-01051-2
Bell M. (2021). The Color Line and the Classroom: Racialized Space and the Making of Neoliberal Schools. Political Economy: Theories, Principles and Politics, 191-213. Nova Science Publishers, Inc..https://doi.org/
