Formalized gender segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[[File:formalized_gender_segregation.png|780x780px]] | [[File:formalized_gender_segregation.png|780x780px]] | ||
This visualization is based on the study [[How_to_cite_Segregation_Wiki| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of | For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | ||
* | * [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | ||
* | * [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | ||
* | * [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | ||
* | * [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
Revision as of 07:48, 10 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1]
2016
United States
Definition
Formalized gender segregation refers to the practice of imposing strict rules and regulations that separate individuals based on their gender, typically in social, educational, or workplace settings. This can include separate facilities, seating arrangements, uniforms, or restrictions on social interaction between genders. The rationale behind formalized gender segregation often stems from cultural, religious, or ideological beliefs that advocate for the preservation of modesty, virtue, or societal harmony.
While proponents argue that formalized gender segregation can help maintain traditional values and ensure decency, critics argue that it reinforces gender-based discrimination and perpetuates inequality. It may limit opportunities for personal growth, equal access to resources, and social integration. Additionally, formalized gender segregation may reinforce stereotypes and contribute to the marginalization of individuals who do not conform to traditional gender norms.
It is important to note that gender segregation practices vary across different cultures and societies. Societies that practice formalized gender segregation often have different perspectives on gender roles, identities, and expectations. However, there is an ongoing global debate about the merits and drawbacks of formalized gender segregation, with proponents advocating for cultural relativism and critics advocating for equal rights and opportunities for all individuals, regardless of their gender.
See also
Related segregation forms
Formalized gender segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
occupational segregation, gender segregation
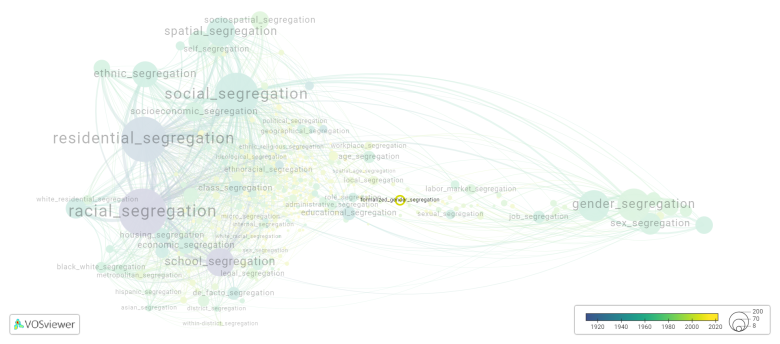
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References
Notes
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Formalized gender segregation appears in the following literature
Joseph L.J., Anderson E. (2016). The influence of gender segregation and teamsport experience on occupational discrimination in sport based employment. Journal of Gender Studies, 25(5), 586-598. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/09589236.2015.1070712
