Blue collar segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
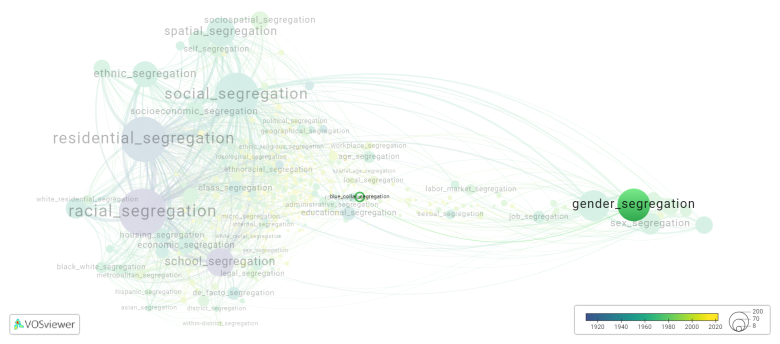
[[File:blue_collar_segregation.png|780x780px]] | [[File:blue_collar_segregation.png|780x780px]] | ||
This visualization is based on the study [[How_to_cite_Segregation_Wiki| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of | For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | ||
* | * [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | ||
* | * [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | ||
* | * [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | ||
* | * [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
Revision as of 07:48, 10 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1]
1986
United States
Definition
Blue collar segregation refers to the practice of separating workers based on their job types, particularly manual labor or low-skilled jobs. This term specifically focuses on the division between white and blue-collar workers. Historically, blue-collar segregation has been prevalent in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and other manual labor-intensive sectors.
Blue-collar segregation can manifest in various ways, including:
1. Economic disparity: Blue-collar workers often face lower wages, fewer benefits, and limited job security compared to white-collar workers.
2. Occupational segregation: Many industries and job roles are predominantly dominated by either white-collar or blue-collar workers. Certain jobs are associated with specific racial or ethnic groups, further contributing to occupational segregation.
3. Geographic segregation: In some cases, blue-collar workers may be concentrated in specific geographic areas or neighborhoods, leading to socio-economic divisions based on job types.
4. Limited social mobility: Blue-collar workers might face barriers to career advancement or upward mobility due to a lack of educational opportunities, skills development, or social networks.
5. Discrimination and bias: Blue-collar workers, particularly those from marginalized communities, may face discrimination based on their job types or wages, perpetuating further segregation and inequality.
Addressing blue-collar segregation requires efforts to promote equal access to education, training, and career development opportunities. Additionally, policies that reduce economic disparities, improve job security, and eliminate discriminatory practices can also help in fostering a more inclusive and equitable workforce.
See also
Related segregation forms
Blue collar segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References
Notes
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Blue collar segregation appears in the following literature
Wharton A.S. (1986). Industry structure and gender segregation in blue collar occupations. Social Forces, 64(4), 1025-1031. https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/64.4.1025