Urban socioeconomic segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===== Date and country of first publication<ref>Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).</ref>===== | ===== Date and country of first publication<ref>Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).</ref>===== | ||
2018<br> | 2018<br> | ||
Iran | Iran; Australia | ||
===== Definition ===== | ===== Definition ===== | ||
Urban | Urban socio-economic segregation refers to the unequal distribution of wealth, resources, and opportunities among different social and economic groups within cities. It refers to the spatial separation of neighborhoods or areas based on income, education level, occupation, race, or ethnicity. | ||
Socio-economic segregation can be seen in various forms, including residential segregation, educational segregation, and employment segregation. It can lead to the concentration of poverty in certain neighborhoods or areas, while wealthier communities have access to better services, schools, and job opportunities. | |||
There are several factors that contribute to urban socioeconomic segregation. historical patterns of discrimination, income inequality, and housing policies play a significant role. Discrimination and segregation practices in the past, such as redlining, have shaped the current patterns of segregated neighborhoods. Additionally, socioeconomic segregation can be reinforced by public policies that prioritize economic development in certain areas, leaving others neglected. | There are several factors that contribute to urban socioeconomic segregation. historical patterns of discrimination, income inequality, and housing policies play a significant role. Discrimination and segregation practices in the past, such as redlining, have shaped the current patterns of segregated neighborhoods. Additionally, socioeconomic segregation can be reinforced by public policies that prioritize economic development in certain areas, leaving others neglected. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
The consequences of urban socioeconomic segregation are wide-ranging. Segregated neighborhoods often lack access to quality education, healthcare, and other essential services. This can perpetuate cycles of poverty and limit upward mobility for individuals living in such areas. Segregated schools may have fewer resources and opportunities, leading to educational disadvantages for students. Furthermore, segregated employment patterns can limit job prospects for individuals living in marginalized areas. | The consequences of urban socioeconomic segregation are wide-ranging. Segregated neighborhoods often lack access to quality education, healthcare, and other essential services. This can perpetuate cycles of poverty and limit upward mobility for individuals living in such areas. Segregated schools may have fewer resources and opportunities, leading to educational disadvantages for students. Furthermore, segregated employment patterns can limit job prospects for individuals living in marginalized areas. | ||
Addressing urban | Addressing urban socio-economic segregation requires comprehensive strategies that tackle root causes and promote equitable access to resources and opportunities. This includes investing in affordable housing options, improving public transportation, implementing fair housing policies, and promoting economic development in underserved areas. Education and awareness about the impact of segregation are also crucial to fostering inclusive communities and reducing inequality in urban areas. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
==Related segregation forms== | |||
Urban socioeconomic segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms: | |||
[[socioeconomic segregation]], [[social segregation]] | |||
[[File:urban_socioeconomic_segregation.png|780x780px]] | |||
This visualization is based on the study [[Segregation_Wiki:About| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
{{NoteAI}} | {{NoteAI}} | ||
==Urban | ==Urban socioeconomic segregation appears in the following literature== | ||
Azhdari A., Sasani M.A., Soltani A. (2018). Exploring the relationship between spatial driving forces of urban expansion and socioeconomic segregation: The case of Shiraz. ''Habitat International'', ''81''(), 33-44. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2018.09.001 | |||
Latest revision as of 07:17, 16 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1][edit | edit source]
2018
Iran; Australia
Definition[edit | edit source]
Urban socio-economic segregation refers to the unequal distribution of wealth, resources, and opportunities among different social and economic groups within cities. It refers to the spatial separation of neighborhoods or areas based on income, education level, occupation, race, or ethnicity.
Socio-economic segregation can be seen in various forms, including residential segregation, educational segregation, and employment segregation. It can lead to the concentration of poverty in certain neighborhoods or areas, while wealthier communities have access to better services, schools, and job opportunities.
There are several factors that contribute to urban socioeconomic segregation. historical patterns of discrimination, income inequality, and housing policies play a significant role. Discrimination and segregation practices in the past, such as redlining, have shaped the current patterns of segregated neighborhoods. Additionally, socioeconomic segregation can be reinforced by public policies that prioritize economic development in certain areas, leaving others neglected.
The consequences of urban socioeconomic segregation are wide-ranging. Segregated neighborhoods often lack access to quality education, healthcare, and other essential services. This can perpetuate cycles of poverty and limit upward mobility for individuals living in such areas. Segregated schools may have fewer resources and opportunities, leading to educational disadvantages for students. Furthermore, segregated employment patterns can limit job prospects for individuals living in marginalized areas.
Addressing urban socio-economic segregation requires comprehensive strategies that tackle root causes and promote equitable access to resources and opportunities. This includes investing in affordable housing options, improving public transportation, implementing fair housing policies, and promoting economic development in underserved areas. Education and awareness about the impact of segregation are also crucial to fostering inclusive communities and reducing inequality in urban areas.
See also[edit | edit source]
Related segregation forms[edit | edit source]
Urban socioeconomic segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
socioeconomic segregation, social segregation
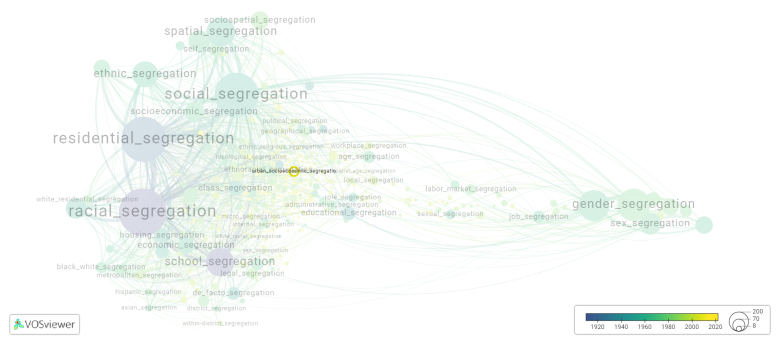
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References[edit | edit source]
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Urban socioeconomic segregation appears in the following literature[edit | edit source]
Azhdari A., Sasani M.A., Soltani A. (2018). Exploring the relationship between spatial driving forces of urban expansion and socioeconomic segregation: The case of Shiraz. Habitat International, 81(), 33-44. Elsevier Ltd.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2018.09.001
