Morphological segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===== Date and country of first publication<ref>Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).</ref>===== | |||
2019<br> | |||
Belgium | |||
===== Definition ===== | |||
Morphological segregation refers to the separation or division of individuals based on physical characteristics or traits, particularly in terms of their morphology or body structure. This can occur within a population or community, where individuals with different morphologies are spatially segregated or occupy different habitats or niches. | Morphological segregation refers to the separation or division of individuals based on physical characteristics or traits, particularly in terms of their morphology or body structure. This can occur within a population or community, where individuals with different morphologies are spatially segregated or occupy different habitats or niches. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 12: | ||
Overall, morphological segregation plays a crucial role in shaping the distribution and interactions of organisms within ecosystems, and understanding its mechanisms and consequences is important for understanding and managing biodiversity. | Overall, morphological segregation plays a crucial role in shaping the distribution and interactions of organisms within ecosystems, and understanding its mechanisms and consequences is important for understanding and managing biodiversity. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
==Related segregation forms== | |||
Morphological segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms: | |||
[[social segregation]], [[sociospatial segregation]] | |||
[[File:morphological_segregation.png|780x780px]] | |||
This visualization is based on the study [[Segregation_Wiki:About| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
== | {{NoteAI}} | ||
==Morphological segregation appears in the following literature== | |||
Bassens D. | Bassens D., van Heur B., Waiengnier M. (2019). Follow the money: cultural patronage and urban elite geographies. ''Urban Geography'', ''40''(5), 719-746. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/02723638.2018.1449429 | ||
Latest revision as of 07:17, 16 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1][edit | edit source]
2019
Belgium
Definition[edit | edit source]
Morphological segregation refers to the separation or division of individuals based on physical characteristics or traits, particularly in terms of their morphology or body structure. This can occur within a population or community, where individuals with different morphologies are spatially segregated or occupy different habitats or niches.
Morphological segregation can be driven by various factors, such as environmental conditions, competition, or natural selection. For example, in a bird population, individuals with different beak shapes may be segregated into different habitats based on their feeding preferences or abilities. Similarly, in a marine ecosystem, fish species with different body shapes may inhabit different depths or areas based on their swimming capabilities or prey preferences.
This phenomenon of morphological segregation can have implications for various ecological processes, including resource partitioning, species coexistence, and community structure. By occupying different ecological niches, individuals with distinct morphologies can exploit different resources and reduce inter-specific competition. This can, in turn, promote species diversity and contribute to the stability of ecological communities.
Overall, morphological segregation plays a crucial role in shaping the distribution and interactions of organisms within ecosystems, and understanding its mechanisms and consequences is important for understanding and managing biodiversity.
See also[edit | edit source]
Related segregation forms[edit | edit source]
Morphological segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
social segregation, sociospatial segregation
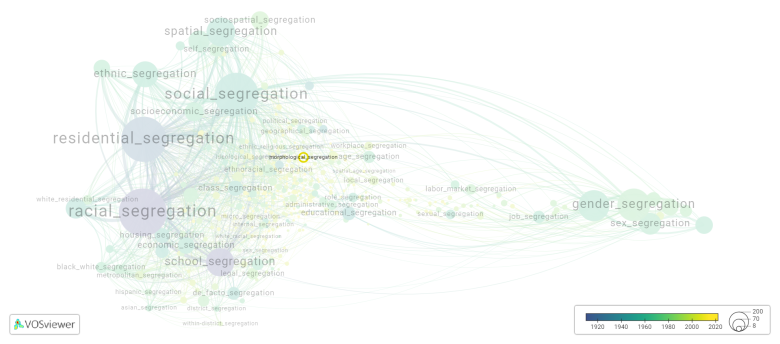
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References[edit | edit source]
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Morphological segregation appears in the following literature[edit | edit source]
Bassens D., van Heur B., Waiengnier M. (2019). Follow the money: cultural patronage and urban elite geographies. Urban Geography, 40(5), 719-746. Routledge.https://doi.org/10.1080/02723638.2018.1449429
