Dynamic segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===== Date and country of first publication<ref>Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).</ref>===== | |||
1999<br> | |||
Brazil | |||
===== Definition ===== | |||
Dynamic segregation refers to the phenomenon where individuals within a group or society voluntarily separate or group themselves based on various characteristics such as race, gender, socio-economic status, or religion. This can occur in various settings such as schools, neighborhoods, workplaces, or social events. | Dynamic segregation refers to the phenomenon where individuals within a group or society voluntarily separate or group themselves based on various characteristics such as race, gender, socio-economic status, or religion. This can occur in various settings such as schools, neighborhoods, workplaces, or social events. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 10: | ||
Efforts to address dynamic segregation may involve promoting diversity and inclusion, creating opportunities for social mixing, challenging stereotypes and biases, and fostering a sense of unity and commonality among different groups. By actively working to break down barriers and increase interactions between diverse individuals, dynamic segregation can be reduced and a more inclusive society can be achieved. | Efforts to address dynamic segregation may involve promoting diversity and inclusion, creating opportunities for social mixing, challenging stereotypes and biases, and fostering a sense of unity and commonality among different groups. By actively working to break down barriers and increase interactions between diverse individuals, dynamic segregation can be reduced and a more inclusive society can be achieved. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
==Related segregation forms== | |||
Dynamic segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms: | |||
[[racial segregation]] | |||
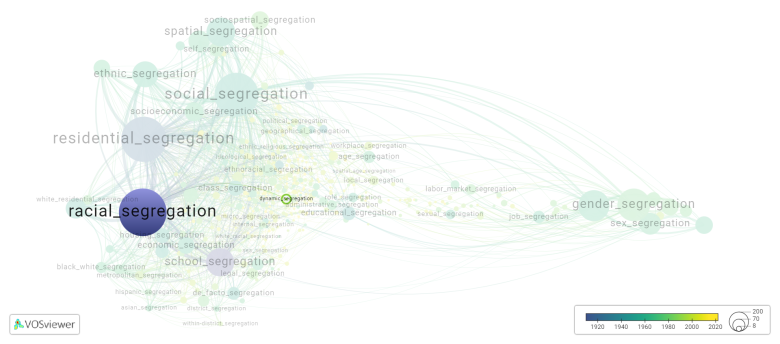
[[File:dynamic_segregation.png|780x780px]] | |||
This visualization is based on the study [[Segregation_Wiki:About| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
== | {{NoteAI}} | ||
==Dynamic segregation appears in the following literature== | |||
Kollmann T., Marsiglio S., Suardi S. (2018). Racial segregation in the United States since the Great Depression: A dynamic segregation approach. ''Journal of Housing Economics'', ''40''(), 95-116. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhe.2018.03.004 | |||
Latest revision as of 07:17, 16 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1][edit | edit source]
1999
Brazil
Definition[edit | edit source]
Dynamic segregation refers to the phenomenon where individuals within a group or society voluntarily separate or group themselves based on various characteristics such as race, gender, socio-economic status, or religion. This can occur in various settings such as schools, neighborhoods, workplaces, or social events.
Dynamic segregation can be influenced by personal preferences, cultural norms, prejudices, or lack of opportunities for integration. It can have both positive and negative impacts, as it can create a sense of belonging and community for some individuals while also perpetuating stereotypes, discrimination, and inequality.
Efforts to address dynamic segregation may involve promoting diversity and inclusion, creating opportunities for social mixing, challenging stereotypes and biases, and fostering a sense of unity and commonality among different groups. By actively working to break down barriers and increase interactions between diverse individuals, dynamic segregation can be reduced and a more inclusive society can be achieved.
See also[edit | edit source]
Related segregation forms[edit | edit source]
Dynamic segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References[edit | edit source]
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Dynamic segregation appears in the following literature[edit | edit source]
Kollmann T., Marsiglio S., Suardi S. (2018). Racial segregation in the United States since the Great Depression: A dynamic segregation approach. Journal of Housing Economics, 40(), 95-116. Academic Press Inc..https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhe.2018.03.004