Multiracial friendship segregation: Difference between revisions
(Creating page) |
(Creating page) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===== Date and country of first publication<ref>Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).</ref>===== | |||
2003<br> | 2003<br> | ||
United States | |||
===== Definition ===== | |||
Multi-racial friendship segregation refers to the phenomenon where people of different racial backgrounds tend to form friendships primarily with others of the same race. This can result in social groups and communities that are racially homogeneous, with limited interaction and friendships across racial lines. | |||
There are several reasons why multiracial friendship segregation can occur. One factor is the tendency for people to feel most comfortable and familiar with others who share similar cultural and ethnic experiences. This is often referred to as homophily, where individuals are naturally drawn towards others who are similar to themselves. It can be easier to establish common ground and bonding when there are shared experiences and cultural references. | There are several reasons why multiracial friendship segregation can occur. One factor is the tendency for people to feel most comfortable and familiar with others who share similar cultural and ethnic experiences. This is often referred to as homophily, where individuals are naturally drawn towards others who are similar to themselves. It can be easier to establish common ground and bonding when there are shared experiences and cultural references. | ||
Another reason for | Another reason for multi-racial friendship segregation is the influence of social networks and the environments we grow up in. People are more likely to form friendships with others who are physically close to them or part of their immediate social circles, such as school or work. If these environments are racially segregated, it can limit opportunities for cross-racial interactions and friendships to form. | ||
Stereotypes and prejudices can also play a role in multiracial friendship segregation. Negative stereotypes or biases towards certain racial groups may discourage individuals from seeking out friendships outside of their own race. It can create barriers and divisions that prevent meaningful connections from developing. | Stereotypes and prejudices can also play a role in multiracial friendship segregation. Negative stereotypes or biases towards certain racial groups may discourage individuals from seeking out friendships outside of their own race. It can create barriers and divisions that prevent meaningful connections from developing. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
There are negative consequences associated with multiracial friendship segregation. It perpetuates existing racial divides and can limit individuals' perspectives and understanding of different cultures. It also reinforces stereotypes and prejudices by preventing people from challenging or debunking them through personal interactions. | There are negative consequences associated with multiracial friendship segregation. It perpetuates existing racial divides and can limit individuals' perspectives and understanding of different cultures. It also reinforces stereotypes and prejudices by preventing people from challenging or debunking them through personal interactions. | ||
Addressing | Addressing multi-racial friendship segregation requires intentional efforts to promote diversity and inclusivity. Creating opportunities for individuals from different racial backgrounds to interact and build relationships can help break down barriers and foster understanding. This can be done through educational initiatives, community programs, or workplace diversity initiatives that encourage cross-cultural interactions. It is also important to challenge stereotypes and prejudices through education and awareness campaigns to promote a more inclusive and unified society. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
==Related segregation forms== | |||
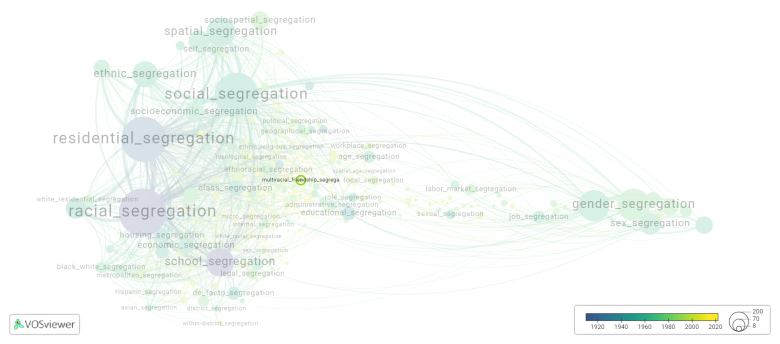
Multiracial friendship segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms: | |||
[[social segregation]] | |||
[[File:multiracial_friendship_segregation.png|780x780px]] | |||
This visualization is based on the study [[Segregation_Wiki:About| The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research]]. | |||
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to: | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2235lkhw First year of publication] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/2d8wg5n3 Louvain clusters] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/223udk5r Betweenness centrality] | |||
* [https://tinyurl.com/244d8unz Disciplines in which segregation forms first emerged (Scopus database).] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
== | ==Notes== | ||
<references /> | |||
{{NoteAI}} | |||
==Multiracial friendship segregation appears in the following literature== | |||
Quillian L. | Quillian L., Campbell M.E. (2003). Beyond black and white: The present and future of multiracial friendship segregation. ''American Sociological Review'', ''68''(4), 540-566. American Sociological Association.https://doi.org/10.2307/1519738 | ||
Latest revision as of 07:17, 16 October 2024
Date and country of first publication[1][edit | edit source]
2003
United States
Definition[edit | edit source]
Multi-racial friendship segregation refers to the phenomenon where people of different racial backgrounds tend to form friendships primarily with others of the same race. This can result in social groups and communities that are racially homogeneous, with limited interaction and friendships across racial lines.
There are several reasons why multiracial friendship segregation can occur. One factor is the tendency for people to feel most comfortable and familiar with others who share similar cultural and ethnic experiences. This is often referred to as homophily, where individuals are naturally drawn towards others who are similar to themselves. It can be easier to establish common ground and bonding when there are shared experiences and cultural references.
Another reason for multi-racial friendship segregation is the influence of social networks and the environments we grow up in. People are more likely to form friendships with others who are physically close to them or part of their immediate social circles, such as school or work. If these environments are racially segregated, it can limit opportunities for cross-racial interactions and friendships to form.
Stereotypes and prejudices can also play a role in multiracial friendship segregation. Negative stereotypes or biases towards certain racial groups may discourage individuals from seeking out friendships outside of their own race. It can create barriers and divisions that prevent meaningful connections from developing.
There are negative consequences associated with multiracial friendship segregation. It perpetuates existing racial divides and can limit individuals' perspectives and understanding of different cultures. It also reinforces stereotypes and prejudices by preventing people from challenging or debunking them through personal interactions.
Addressing multi-racial friendship segregation requires intentional efforts to promote diversity and inclusivity. Creating opportunities for individuals from different racial backgrounds to interact and build relationships can help break down barriers and foster understanding. This can be done through educational initiatives, community programs, or workplace diversity initiatives that encourage cross-cultural interactions. It is also important to challenge stereotypes and prejudices through education and awareness campaigns to promote a more inclusive and unified society.
See also[edit | edit source]
Related segregation forms[edit | edit source]
Multiracial friendship segregation is frequently discussed in the literature with the following segregation forms:
This visualization is based on the study The Multidisciplinary Landscape of Segregation Research.
For the complete network of interrelated segregation forms, please refer to:
References[edit | edit source]
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Date and country of first publication as informed by the Scopus database (December 2023).
At its current state, this definition has been generated by a Large Language Model (LLM) so far without review by an independent researcher or a member of the curating team of segregation experts that keep the Segregation Wiki online. While we strive for accuracy, we cannot guarantee its reliability, completeness and timeliness. Please use this content with caution and verify information as needed. Also, feel free to improve on the definition as you see fit, including the use of references and other informational resources. We value your input in enhancing the quality and accuracy of the definitions of segregation forms collectively offered in the Segregation Wiki ©.
Multiracial friendship segregation appears in the following literature[edit | edit source]
Quillian L., Campbell M.E. (2003). Beyond black and white: The present and future of multiracial friendship segregation. American Sociological Review, 68(4), 540-566. American Sociological Association.https://doi.org/10.2307/1519738